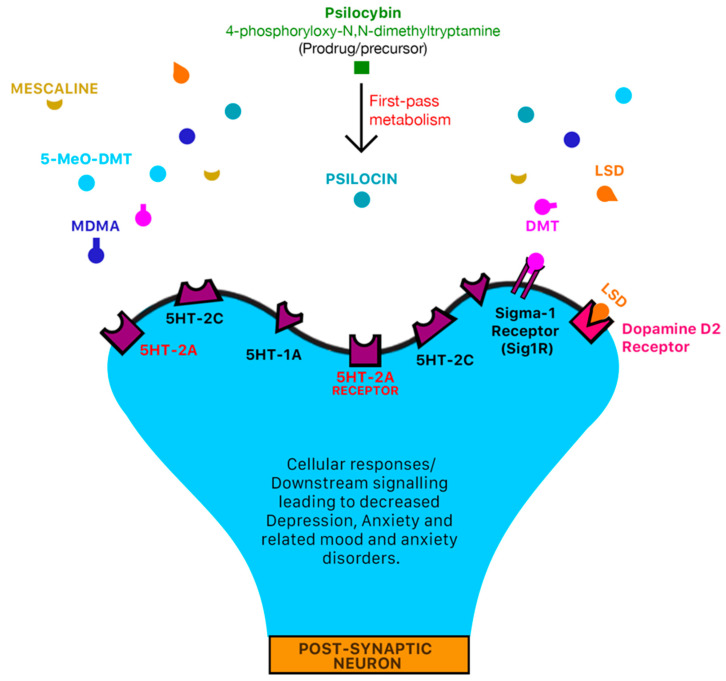
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of classic serotonergic drugs. 5-HT serotonin receptors are densely located in areas of the brain that are responsible for mediation of mood and anxiety disorders such as the pre-frontal cortex [18,24]. Classic serotonergic psychedelic drugs such as LSD, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT, mescaline, psilocybin and MDMA all have an affinity for serotonergic 5-HT receptors [17] which may mediate the psychotomimetic and pharmacological effects of psychedelic drugs. LSD may also interact with dopamine D2 receptors and trace-amine associated receptors (TAARs) to produce psychotomimetic and pharmacological effects [22]. DMT also interacts agonistically with the sigma-1 receptor (Sig1R) [22,23] and trace-amine associated receptors (TAARs) to produce anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects [22]. In pre-clinical animal models, trace-amine associated receptors such as TAAR1 have been identified as a novel target for metabolic disorders, drug addiction, neurological and psychiatric diseases such as depression and schizophrenia [25,26,27,28].