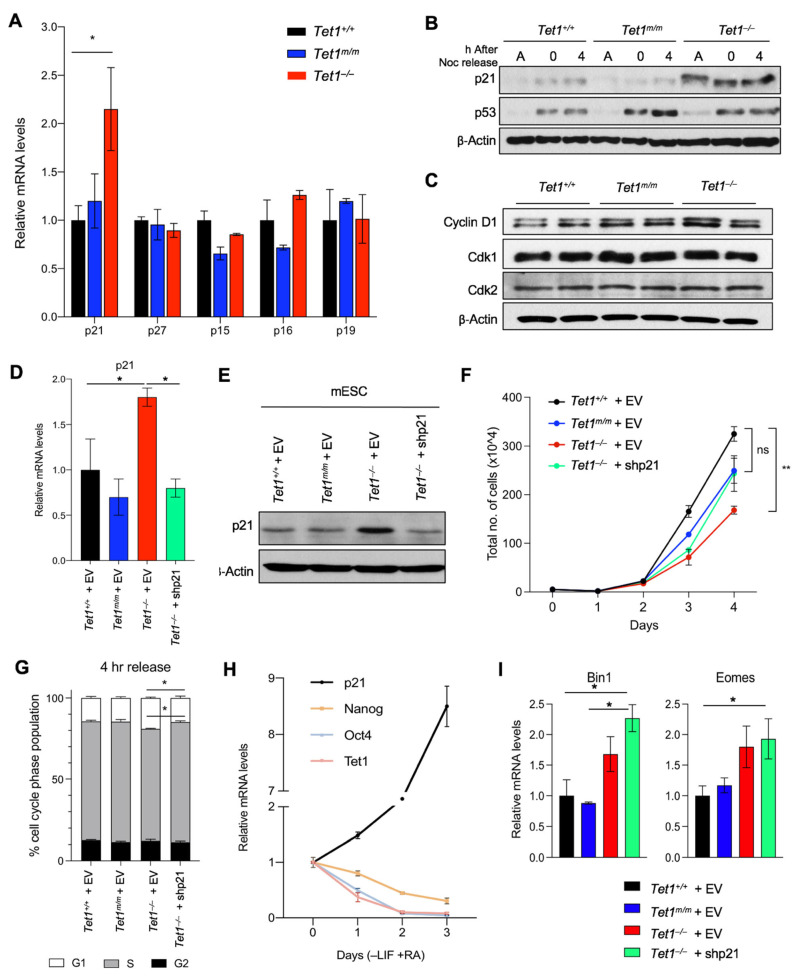
Figure 2.
Aberrant upregulation of p21 is responsible for the slow proliferation of Tet1−/− mESCs. (A) Quantification of p21, p27, p15, p16 and p19 mRNA levels in mESCs of indicated genotypes by RT-qPCR. Data normalized to Gapdh expression. Three lines of each genotype were used. (B) Quantification of p21 and p53 protein levels in asynchronous (A), G2/M-arrested (0 h) and released (4 h) mESCs of indicated genotypes by Western blot analysis. β-actin was used as a loading control. (C) Quantification of Cdk1, Cdk2 and Cyclin D1 protein levels in asynchronous mESCs of indicated genotypes by Western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control. (D,E) Quantification of p21 mRNA levels by RT-qPCR (D) and protein levels by Western blot (E) in Tet1+/+, Tet1m/m, Tet1−/− mESCs transduced with empty vector (EV) or an shRNA against p21 vector (shp21). (F) Growth curve of mESCs transduced with an empty vector (EV) or an shRNA against p21 vector (shp21) over a 4-day period. (G) The percentage of mESCs of indicated genotypes expressing empty vector (EV) or an shRNA against p21 (shp21) in each phase of the cell cycle 4 h after release from Nocodazole block. (H) Quantification of mRNA levels of p21, Tet1 and pluripotency markers (Oct4 and Nanog) by RT-qPCR in wild type mESCs differentiated (−LIF +RA) for three days. Three independent mESC lines were used. (I) Quantification of mRNA levels of mesoderm markers Bin1 and Eomes by RT-qPCR in Tet1+/+, Tet1m/m and Tet1−/− mESCs expressing empty vector (EV) or an shRNA against p21 (shp21) and cultured in mESC media. Three replicates of each genotype were used. In all panels, data are presented as ± SEM; statistically significant ** p < 0.01 and * p < 0.05 (two-way ANOVA test).