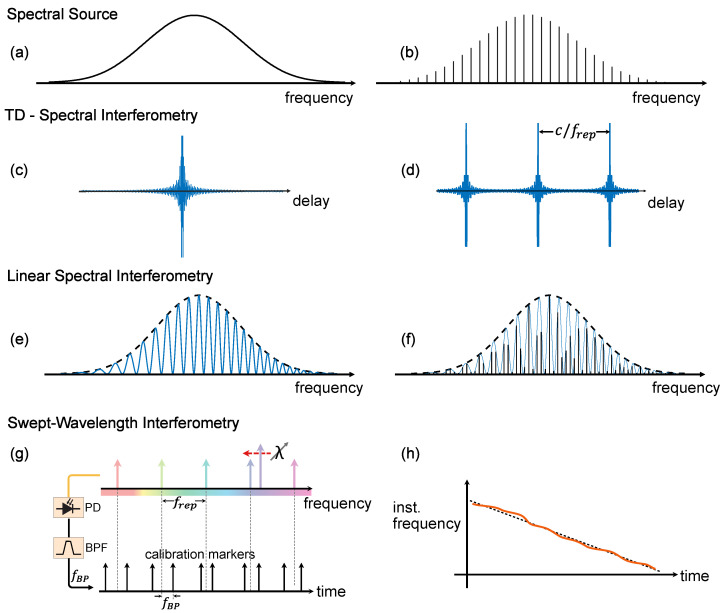
Figure 2.
Comparison between spectral sources and the interferometric signals obtained with different configurations. (a,b) Spectral sources. (c,d) Time domain-spectral interferometry (TD- SI). (e,f) Linear spectral interferometry. (g,h) Frequency comb assisted laser calibration for SWI. Broadband sources are exemplified with a continuous (a) and discrete nature (b). The interferogram using a TD approach based on white light is single burst when the difference of the optical path is zero (c). In contrast, if a frequency comb is employed, the interferogram pattern consists of several bursts spaced by (d). The interference signal using an SDI approach is measured with a CCD camera when using a conventional source (e) and discrete distribution of spectral components is recorded when using a frequency comb (f). In (g), a sweeping laser is heterodyned against the frequency comb of repetition rate . Calibration markers are detected every time the scanning laser is (central frequency of the bandpass filter) away from the comb line. Beats notes are unevenly spaced for the laser being swept nonlinearly. (h) Calibrated instantaneous laser frequency (orange trace) on the top of linear approximation (dotted line).