Figure 1. Role of ATR/CHK1 pathway in homologous recombination repair.
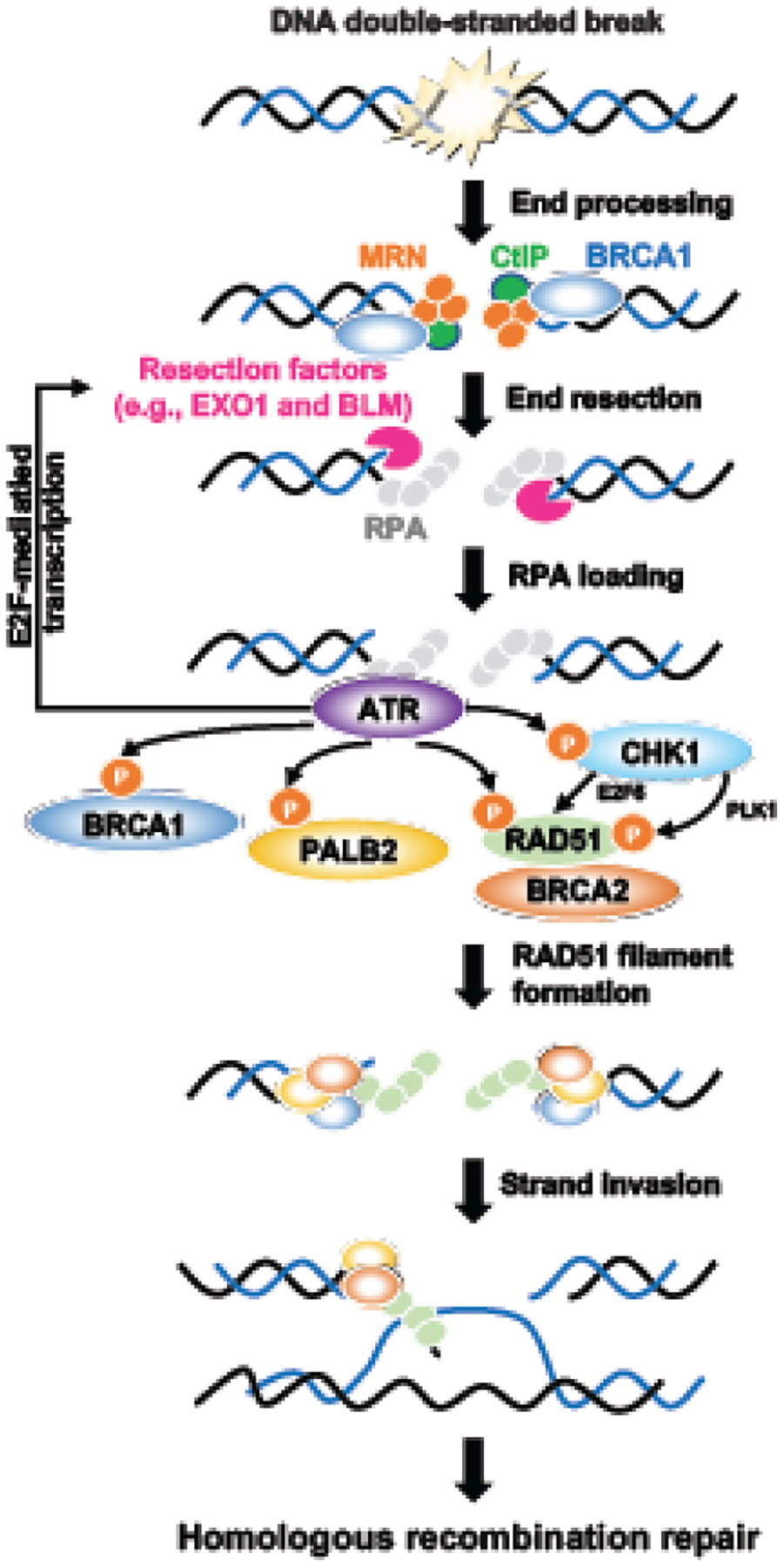
During homologous recombination repair, the double-stranded break is recognized by the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 (MRN) complex, CtIP, and BRCA1, which resects DNA with EXO1 and BLM helicase to create 3’-overhang single-stranded DNAs. The single-stranded DNAs will be protected by RPA, which further activates the ATR/CHK1 pathway. ATR promotes HR repair by phosphorylating key HR proteins, including BRCA1, PALB2, and RAD51. ATR also maintains the pool of resection factors by promoting E2F-mediated transcription. CHK1 mainly assists HR repair by phosphorylating RAD51 via PLK1 or promoting E2F6-mediated RAD51 transcription. The BRCA1-PALB2-BRCA2 complex then mediates the replacement of RPA by RAD51. RAD51 filaments further invade the complementary DNA template, leading to branch migration, resolution, and faithful DNA repair.
