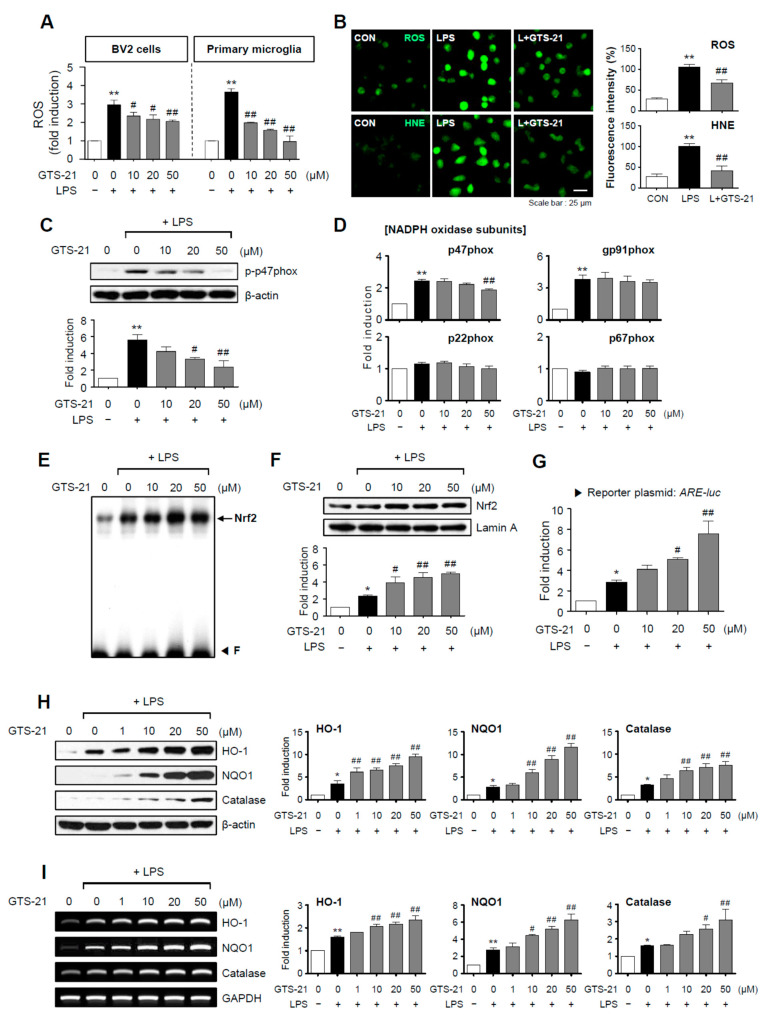
Figure 3.
GTS-21 inhibited the production of ROS and HNE by inhibiting the NADPH oxidase subunit p47phox and increasing Nrf2/ARE signaling. (A) GTS-21 was applied to microglial cells 1 h before LPS stimulation for 16 h, and intracellular ROS levels were measured using the DCF-DA method (n = 4). (B) A representative confocal image of CellROX-derived fluorescence generated by intracellular ROS, and immunofluorescence staining for HNE in BV2 cells (n = 4). (C) Phosphorylation of the p47phox subunit was determined using western blot analysis (n = 3). (D) Quantitative RT-PCR to determiner mRNA expression level of NADPH oxidase subunits in BV2 microglia (n = 3–4 per group). (E) EMSA to assess the DNA binding activity of Nrf2. (F) The nuclear translocation of Nrf2 was assessed by western blot analysis (n = 3). (G) ARE-luc reporter gene activity after transient transfection (n = 3). (H,I) Effects of GTS-21 on the protein and mRNA expressions of HO-1, NQO1, and catalase in BV2 cells (n = 3). Western blot (H) and RT-PCR (I) data are shown. The left panel shows representative blots/gels, whereas the right panel shows quantitative data. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, vs. control group; ** p < 0.01, vs. control group; # p < 0.05 vs. LPS-treated group; ## p < 0.01 vs. LPS-treated group.