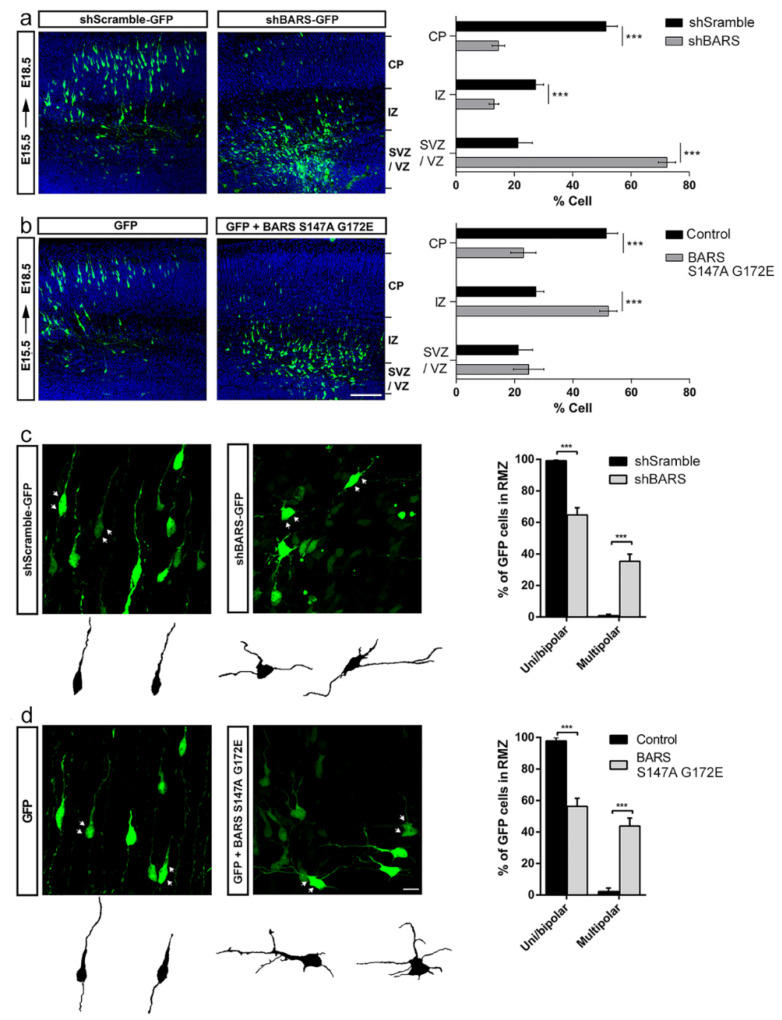
Figure 3.
BARS regulates migration and multipolar-to-bipolar transition in cortical neurons in situ. (a) Left and middle panels: representative images of coronal cortical slices of mouse brain (embryonic day E18.5), expressing sc-shRNA-BARS-GFP (shScramble) or shRNA-BARS-GFP (shBARS) after IUE; right panel: quantification (%) of GFP-positive electroporated neurons by layers. VZ: ventricular zone, SVZ: subventricular zone, IZ: intermediate zone, CP: cortical plate. (b) Idem to previous panels, but after IUE of GFP or GFP + BARS S147A G172E; right panel: quantification (%) of GFP-positive electroporated neurons by layers. VZ: ventricular zone, SVZ: subventricular zone, IZ: intermediate zone, CP: cortical plate. Scale bar 100 µm. (c) Left and middle panels: High magnification confocal images of cortical neurons expressing either sc-shRNA-BARS-GFP (shScramble) or shRNA-BARS-GFP (shBARS) at radial migration zone, RMZ; right panel: quantification (%) of uni/bipolar and multipolar morphologies in shScramble- and shBARS-expressing neurons. (d) Left and middle panels: high magnification confocal images of cortical neurons expressing either GFP or GFP + BARS S147A G172E. Scale bar: 10 µm; right panel: quantification (%) of uni/bipolar and multipolar in GFP- and BARS S147A G172E-expressing neurons. For all experiments 10 slices were analyzed from 3 independent IUE for each experimental condition. Graphs represent mean ±S.E.M.; *** p < 0.001, Student’s t-test.