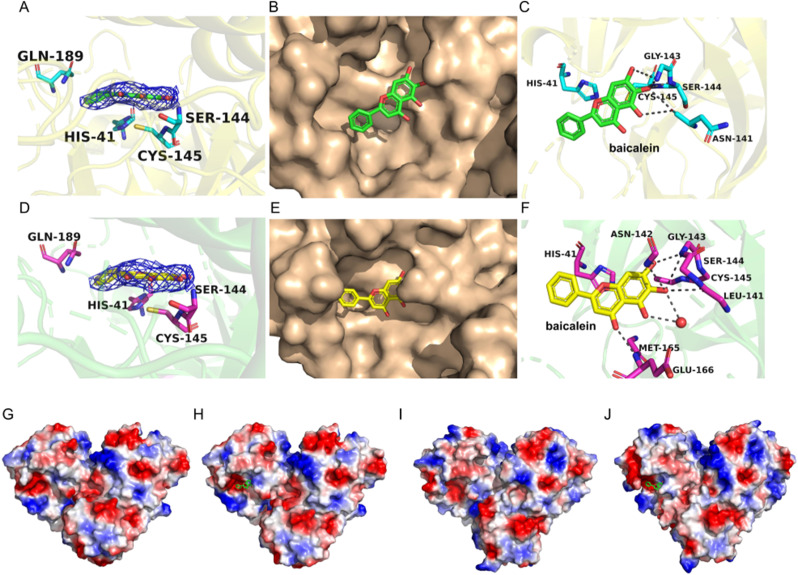
Fig. 3.
Crystal structures of SARS-CoVs with baicalein. (A) Electron density maps (2Fo-Fc) of baicalein at 1.0 σ (7XAX). (B) Baicalein (green) in the active site of SARS-CoV Mpro. (C) Hydrogen bonding (dashed lines) interactions between SARS-CoV Mpro and baicalein. (D) Electron density maps (2Fo-Fc) of baicalein at 1.0 σ (6M2N). (E) Baicalein (yellow) in the active site of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. (F) Hydrogen bonding (dashed lines) interactions between SARS-CoV-2 Mpro and baicalein. (G) Electrostatic potential surface distribution of SARS-CoV-apo. (H) Electrostatic potential surface distribution of SARS-CoV Mpro-baicalein. (I) Electrostatic potential surface distribution of SARS-CoV-2-apo. (J) Electrostatic potential surface distribution of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro-baicalein. The color of the surface denotes the electrostatic potential, while red signififies negative charge and blue signififies positive charge. Baicalein is shown in sticks (green). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)