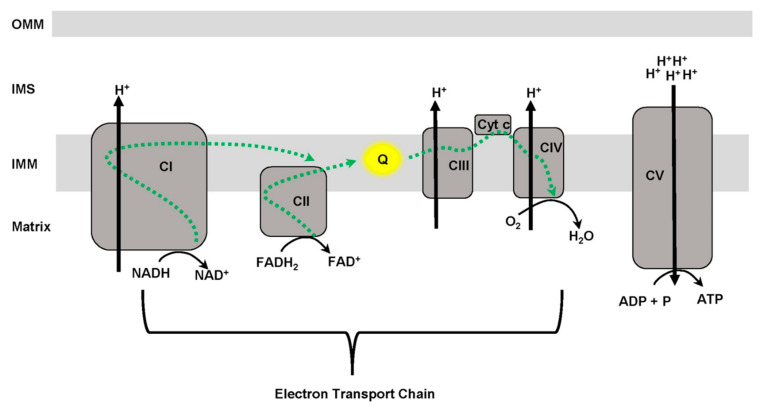
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). A mitochondrion is comprised of an outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM), intermembrane space (IMS), inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) and matrix. Electrons from NADH and FADH2 enter the electron transport chain (ETC) at complex I (CI) and complex II (CII), respectively, and are passed to ubiquinone (Q), which then transfers electrons to complex III (CIII). Cytochrome c (Cyt C) transfers electrons from CIII to complex IV (CIV) where O2 as the final electron acceptor is reduced to H2O. The movement of electrons along the electron transport chain (ETC) results in protons (H+) being pump out from the matrix to the IMS at CI, CIII, and CIV. Ultimately, protons are channeled back into the matrix through complex V (CV) where ADP and P are coupled to form ATP.