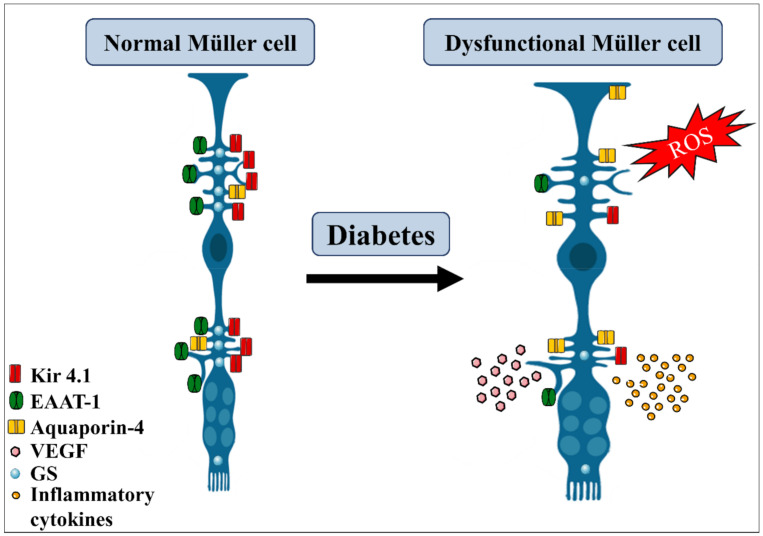
Figure 4.
Diabetes effects on Müller glia. Diabetic condition triggers several morphological and metabolic alterations in Müller glia cells. They become hypertrophic, suffer increase in aquaporin-4, decrease the expression of Kir4.1 channel, glutamine synthetase (GS), and EAAT-1 transporters, thus affecting the regulation of the ionic balance and glutamate uptake. Under this condition, Müller glia also increase the production of reactive oxidative species (ROS) and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and VEGF, contributing to retinal damage. EAAT, excitatory amino acid transporter. Adapted from smart.servier.com (accessed on 1 April 2021).