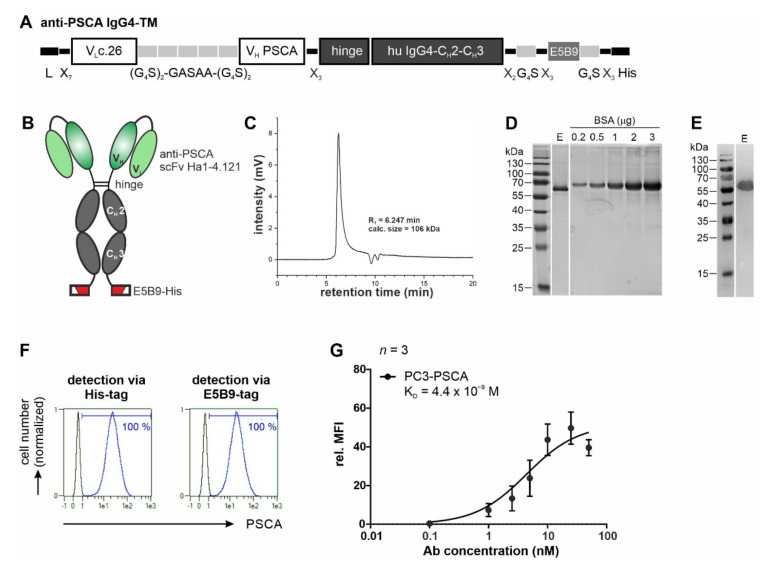
Figure 2.
Biochemical characterization and binding properties of the recombinant anti-PSCA IgG4-TM. (A) The anti-PSCA scFv Ha1-4.1.2c.26 was fused to the hinge and Fc-region of human IgG4 molecules via flexible peptide linkers. In addition, the E5B9- and His-tag were fused to the C-terminus of the recombinant Ab. (B) The anti-PSCA IgG4-TM forms homodimers that are covalently connected via disulfide bounds in the hinge region. L, leader peptide; VL, variable domain of the light chain; VH, variable domain of the heavy chain; CH, constant domain of the heavy chain; scFv, single-chain fragment variable. (C–E) After purification via protein A affinity chromatography, the elution fraction (E) containing the anti-PSCA IgG4-TM was analyzed via (C) SE-HPLC and (D,E) SDS-PAGE. (D) Proteins (TM monomer, Mw = 56 kDa) separated via SDS-PAGE were stained via Quick Coomassie® Stain solution to determine TM purity and concentration by means of a BSA standard. (E) After Western blotting, the anti-PSCA IgG4-TM was detected via its C-terminal His-tag. Uncropped WB in Figure S1. (F,G) Binding activity of the anti-PSCA IgG4-TM was evaluated by flow cytometry. PC3-PSCA cells were incubated with (F) 20 ng/µL or (G) increasing TM concentrations. Binding was detected via anti-His-PE Ab or primary anti-La(5B9) mAb, and secondary PE goat anti-mouse IgG (minimal x-reactivity) Ab. (F) Histograms show percentage of stained cells (blue graphs) in comparison to the respective negative controls (black graphs). (G) For calculation of affinity towards PSCA, Ab concentrations were plotted against the relative mean fluorescence intensity (rel. MFI) values. Results of three independent experiments are shown (rel. MFI ± SEM).