Fig. 2.
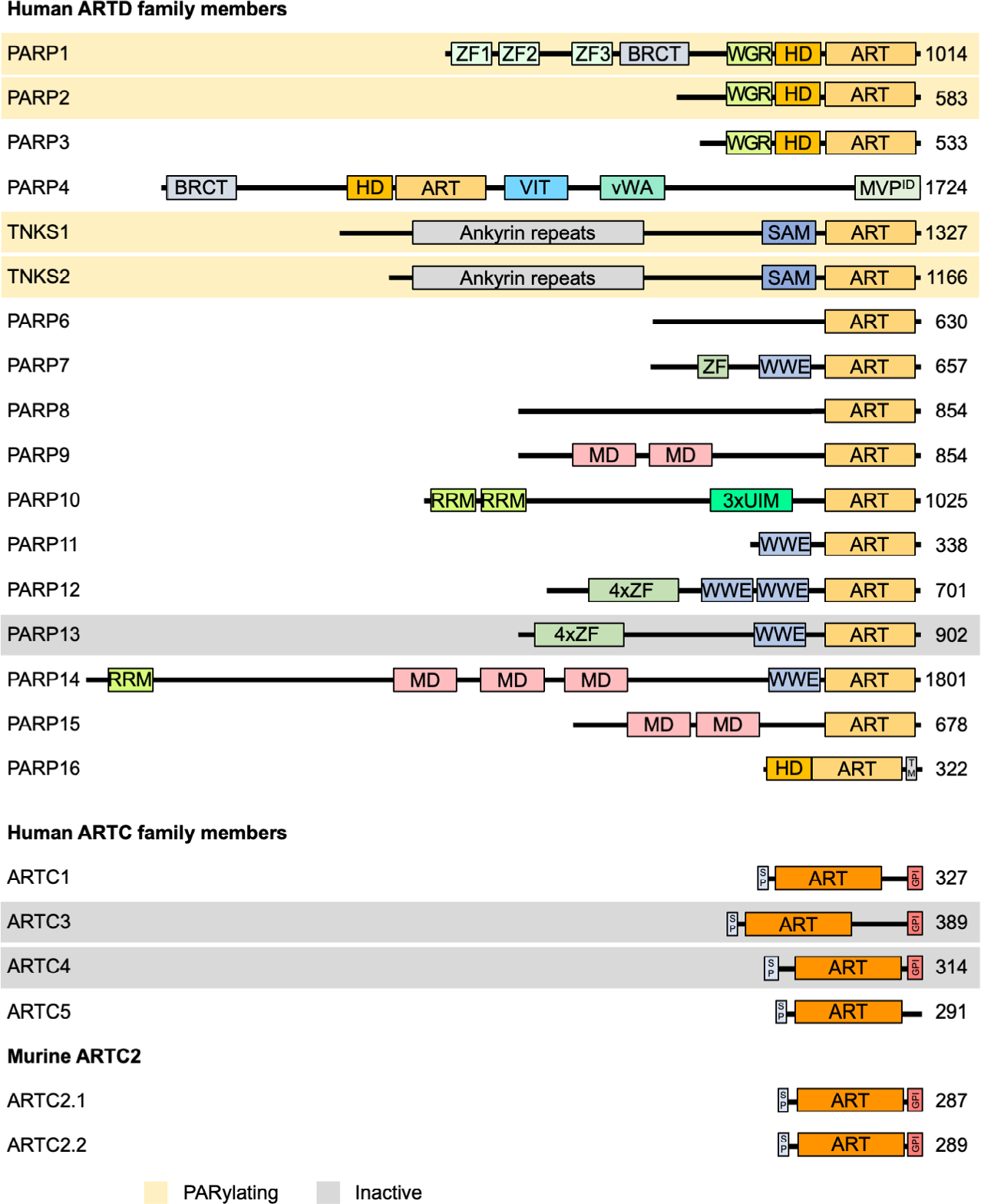
Domain architecture of ARTD and ARTC family members. Important domains of ARTDs and ARTCs family members are indicated. PARylating members as well as members that have been suggested to be catalytically inactive are highlighted in orange and gray, respectively. All other proteins possess MARylating activity. As discussed in the text, whether PARP9 is active has not been fully clarified. The potential coding region of human ARTC2 carries premature stop codons, displayed are the two proteins expressed from two closely related murine genes. ART, ADP-ribosyltransferase domain; BRCT, BRCA1 C terminus domain; GPI, glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor; HD, helical domain; MD, macrodomain; MVPID, major vault protein interaction domain; RRM, RNA-recognition motif; SAM, sterile alpha motif; SP, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane motif; UIM, ubiquitininteraction motif; vWA, von Willebrand factor type A domain; WGR, conserved Trp-Gly-Arg motif domain; WWE, three conserved residues Trp-Trp-Glu motif domain; ZF, Zinc finger (light green, CCHC-type ZnF1 and ZnF2, CCCC-type ZnF3; purple, CCCH-type ZnF).
