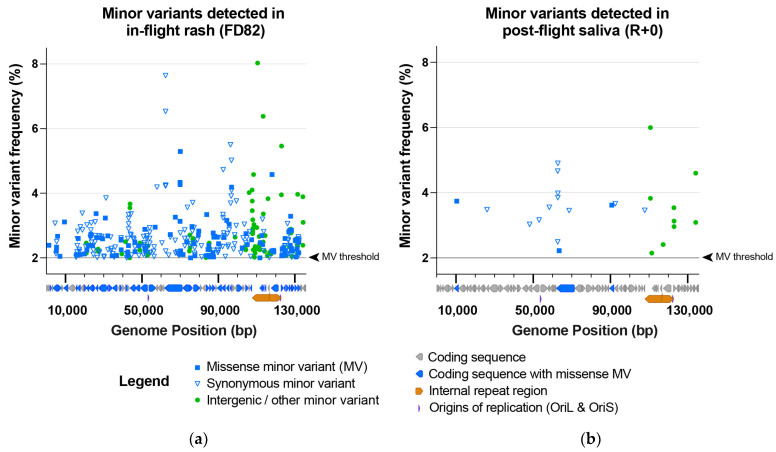
Figure 5.
The in-flight rash (FD82) HSV-1 sample contained far more minor variants in the viral genome population than the post-flight saliva (R + 0) HSV-1 sample. This included (a) 366 MVs in the in-flight rash vs. (b) 24 in the post-flight saliva HSV-1 samples. Minor variants (MVs) are plotted based on their location within the HSV-1 genome (x-axis) and the frequency of the detected MV allele (y-axis) at each position. Minor variants are color-coded according to their classification as missense (genic), synonymous (genic), or intergenic/other. A black line and arrowhead (right of each plot) indicate the MV detection threshold of 2% (0.02). A diagram of HSV-1 coding sequences is located below each x-axis to highlight the coding sequences that contain missense minor variants. Supplementary Table S3 includes the precise location, coverage depth (i.e., forward and reverse reads supporting the major vs. the minor allele), and a list of specific MV impacts within each gene.