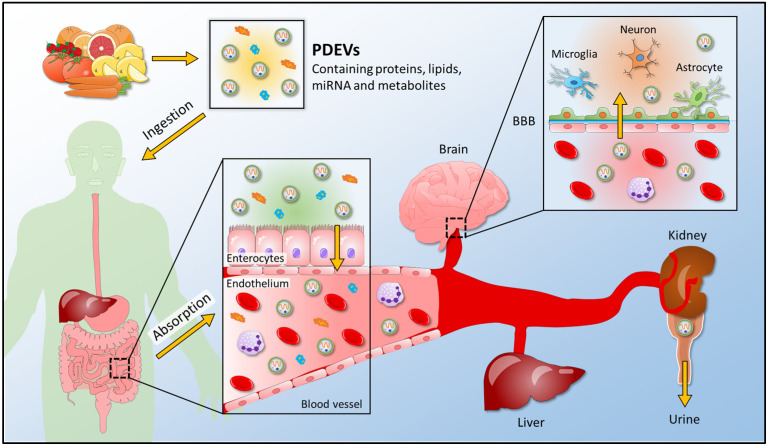
Figure 4.
A schematic view for the uptake of plant-derived extracellular vesicles into the human body. PDEVs containing proteins, lipids, miRNA, and metabolites enter the human body after edible plant ingestion. In the gastrointestinal tract, where food is digested, PDEVs are absorbed and enter the bloodstream; thus, reaching the final recipient organs, such as the brain, liver, and kidney. PDEVs release their content in target organs and exert their biological properties. They can cross the BBB and reach the cells of the central nervous system, or they can be found in the urine of plant-eating humans. PDEVs, plant-derived extracellular vesicles; BBB, blood-brain barrier.