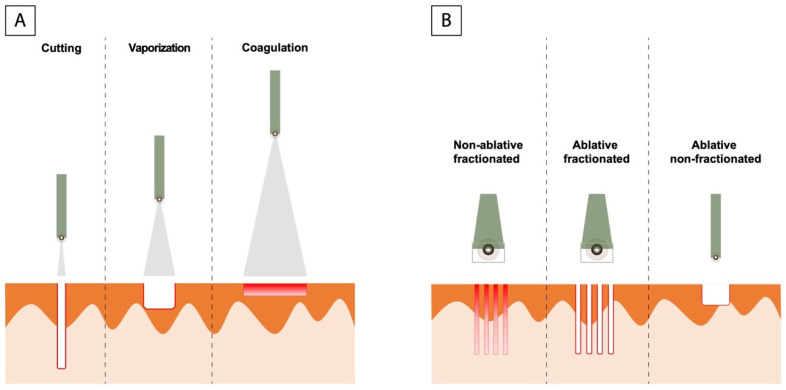
Figure 2.
(A) Focused light with a very small beam of incidence on the skin (0.1–1 mm) causing pinpoint injury, which allows us to use it as a cutting system for cutting. Separating the laser handpiece from skin we produce a larger spot (2–5 mm), increasing the area of laser-tissue interaction, and thus vaporizes the tissues. Finally, a large spot size (4 mm) causes a drop in irradiance, resulting in non-ablative coagulation, which allow hemostasis of small bleeding vessels. (B) Types of CO2 laser: Non fractionated laser acts on the entire treated area, however fractionated lasers treat only small columns of the treated skin, known as microthermal zones (MTZs). These MTZs can be non-ablative dermal injuries or both epidermal and dermal injuries in case of ablative fractionated laser.