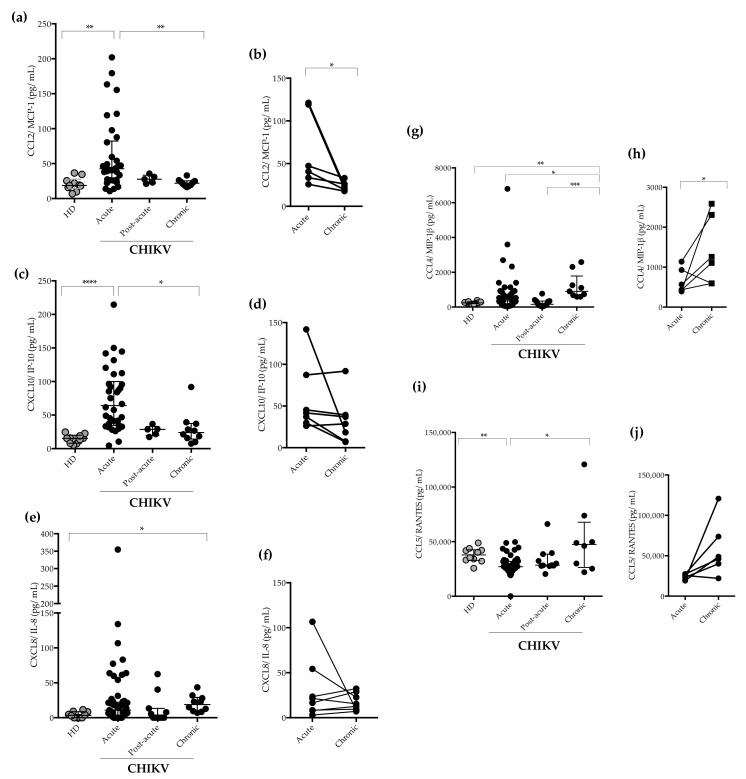
Figure 4.
Circulating plasma levels of chemokines CCL2/MCP-1, CXCL10/IP-10, CXCL8/IL-8, CCL4/MIP1-β, and CCL5/RANTES (pg/mL) in CHIKV-infected patients. (a) Quantification of the plasma levels of CCL2/MCP-1during acute (n = 34), post-acute (n = 5), and chronic phase (n = 10). Healthy donors (HD) (n = 10). (b) CCL2/MCP-1 levels in paired samples acute vs. chronic. (c) Quantification of the plasma levels of CXCL10/IP-10 during acute (n = 34), post-acute (n = 5), and chronic phase (n = 10). Healthy donors (HD) (n = 10). (d) CXCL10/IP-10 levels in paired samples acute vs. chronic. (e) CXCL8/IL-8 levels during acute (n = 60), post-acute (n = 11), and chronic phase (n = 10). Healthy donors (HD) (n = 10). (f) CXCL8/IL-8 levels in paired samples acute vs. chronic. (g) Quantification of the plasma levels of CCL4/MIP1-β during acute (n = 57), post-acute (n = 12), and chronic phase (n = 9). Healthy donors (HD) (n = 10). (h) CCL4/MIP1-β levels in paired samples acute vs. chronic. (i) Quantification of the plasma levels of CCL5/RANTES during acute (n = 49), post-acute (n = 11), and chronic phase (n = 8). Healthy donors (HD) (n = 10). (j) CCL5/RANTES levels in paired samples acute vs. chronic. For the statistical analysis, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank, Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn’s multiple comparisons tests were performed. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, and **** p ≤ 0.0001. Median and interquartile range (IQR).