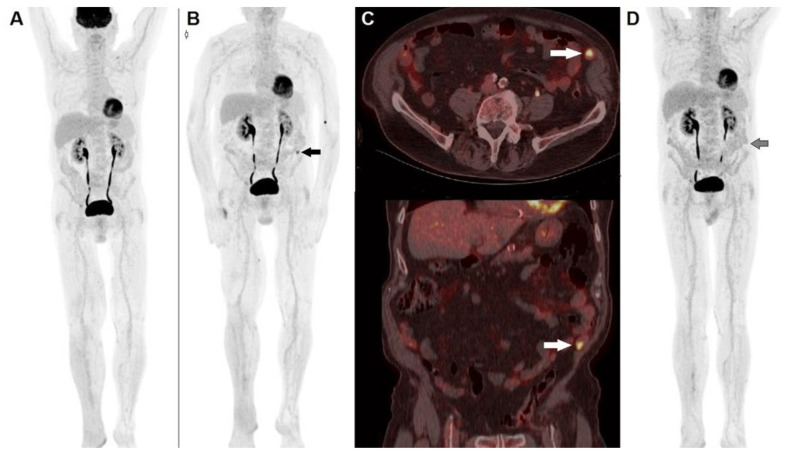
Figure 2.
A 74-year-old male, previously submitted to excision of nodular cutaneous melanoma of the right foot (Breslow thickness of 8 mm, Clark level IV, stage pT4a), performed 18F-FDG PET/CT before the start adjuvant immunotherapy. (A) MIP image showed physiological tracer biodistribution, with no evidence of pathological accumulation. PET/CT MIP (B) performed after 3 months of PD-1 blocker (nivolumab) depicted the appearance of an area of increased tracer accumulation in the left iliac fossa (black arrow). (C) Fused corresponding PET/CT axial (upper row) and coronal (lower row) of the abdominal region demonstrated the onset of a hypermetabolic nodule next to the abdominal wall, suspected to be peritoneal localization (white arrow). The pattern was interpreted according to PERCIMT criteria (i.e., pseudo-progression) and the patient continued immune check-point inhibitor. A further PET/CT MIP (D) after 6 weeks demonstrated complete spontaneous regression of the area of increased 18F-FDG accumulation in the left iliac fossa (black arrow), thus confirming the diagnosis of pseudo-progression.