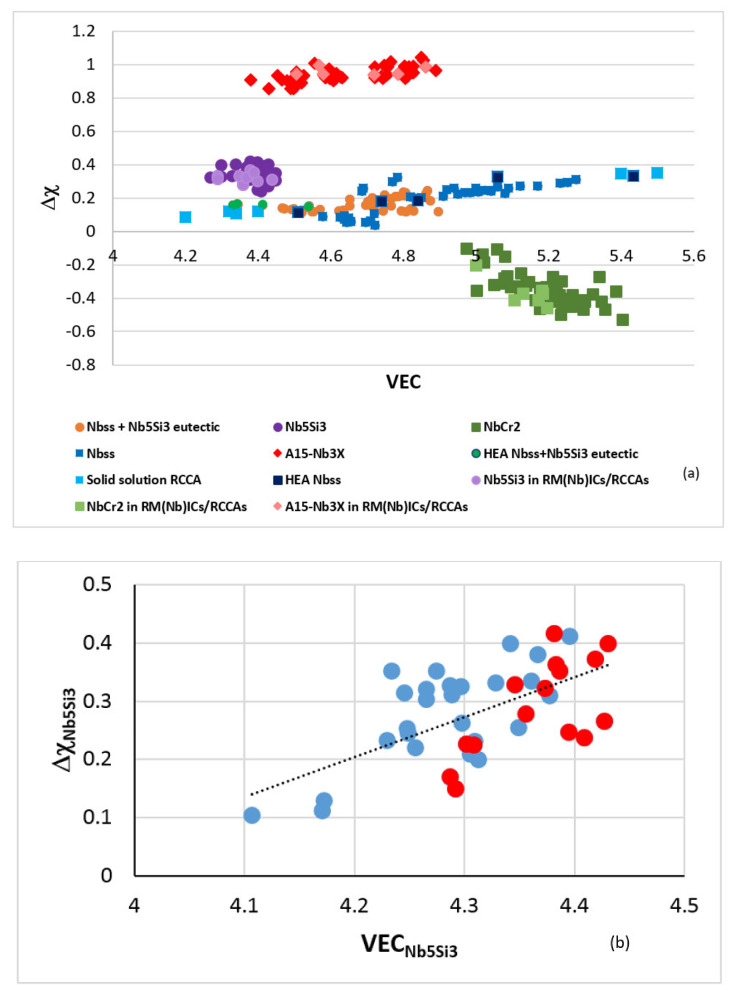
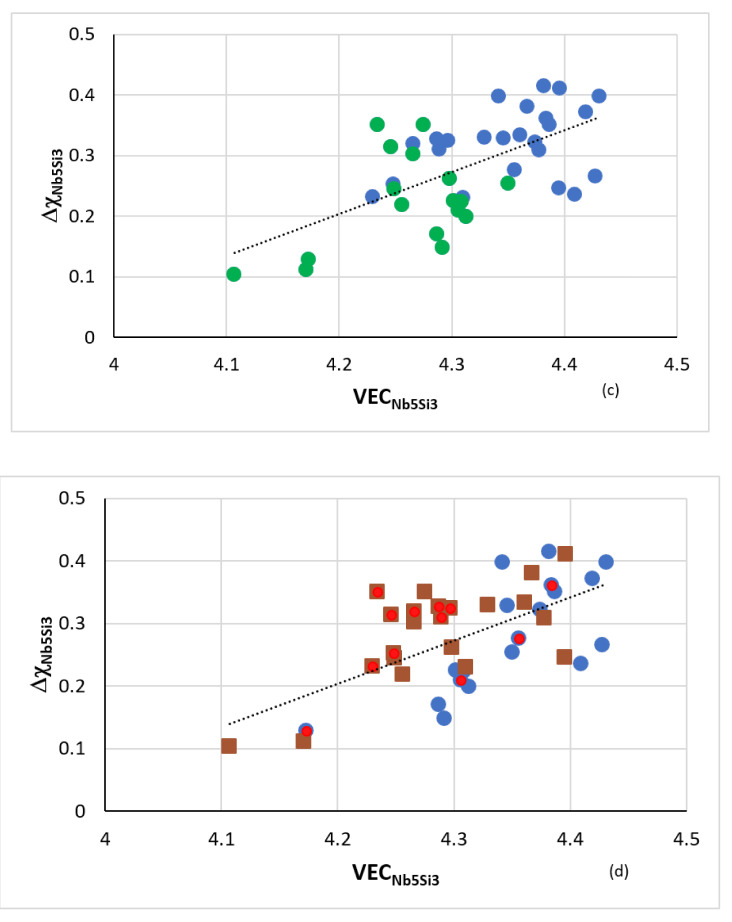
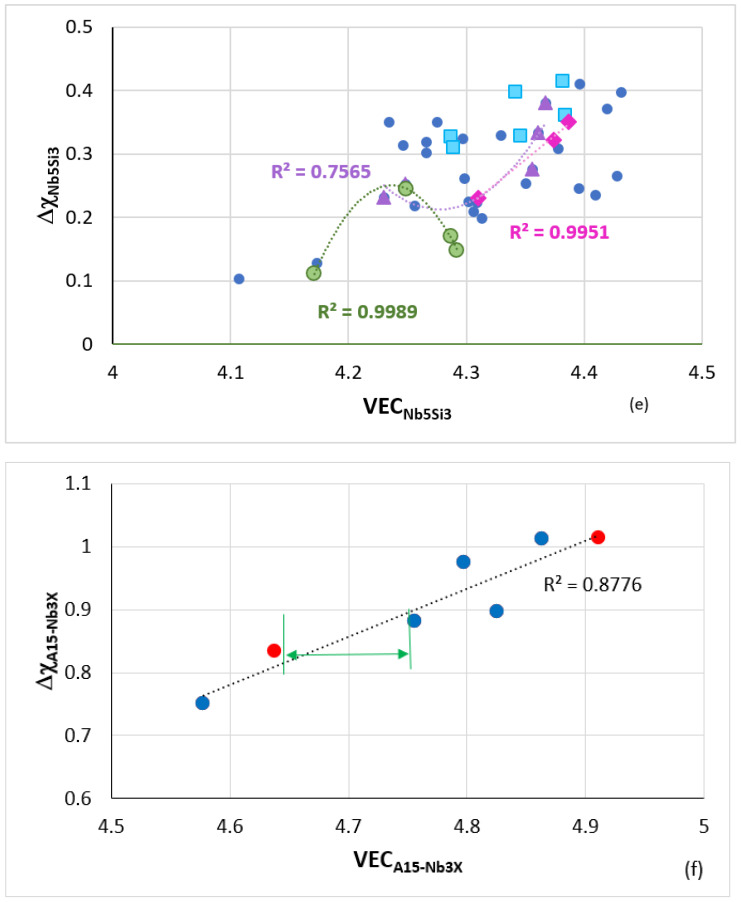
Figure 3.
(a) Δχ versus VEC map of phases in RM(Nb)ICs, RM(Nb)ICs/RCCAs, and single-phase RCCAs. The single-phase RCCAs contain Nb but not Si. The data is for bcc Nbss [8], Nb5Si3 [9], C14-NbCr2 Laves [14], eutectics of bcc Nbss + βNb5Si3 [15], A15-Nb3X [14], the bcc solid solution RCCAs studied by Senkov et al. [2], the HEA bcc Nbss, and the HEA bcc Nbss + βNb5Si3 eutectics in RM(Nb)ICs [1,15]. The RCCAs with high VEC values are the NbMoTaW and NbMoTaWV alloys [2], the RCCAs with lower VEC values have Al, Nb and Ti additions with/without Hf [2]. (b–e) Δχ versus VEC maps of alloyed tetragonal Nb5Si3 in RM(Nb)ICs and RM(Nb)ICs/RCCAs. (b) shows high-entropy silicides (blue circles) and complex concentrated silicides (red circles). In (c), the B-alloyed T2-Nb5(Si,B)3 silicides are shown with green circles. In (d) the Ti-rich Nb5Si3 is shown with brown squares and the Hf-rich Nb5Si3 with red circles (note that the Nb5Si3 can be Ti-rich or Hf-rich or Ti and Hf-rich (e.g., see [9,19,20,21,25,26]), the latter is the case when the metallic UHTM contains both elements). In (b–d) the dashed lines are drawn to help the eye see the trend in the data. In (e), the tetragonal Nb5Si3 that is alloyed with B, Ge, Sn or Ge + Sn is shown with light green circles, light blue squares, purple triangles, and pink diamonds, respectively. The data for the alloyed tetragonal Nb5Si3 is for the alloys EZ8, JG2, JN1, KZ6, OHS1, TT4, TT5, TT6, TT7, TT8, ZF6, ZF9, and ZX8 (see Appendix A for the nominal compositions). (f) Δχ versus VEC map of alloyed A15-Nb3X in RM(Nb)ICs, and RM(Nb)ICs/RCCAs. The data is for the A15 compounds in the Table 1. The blue circles indicate A15-Nb3X high entropy compounds. The gap in VEC values is shown with the green double arrow.