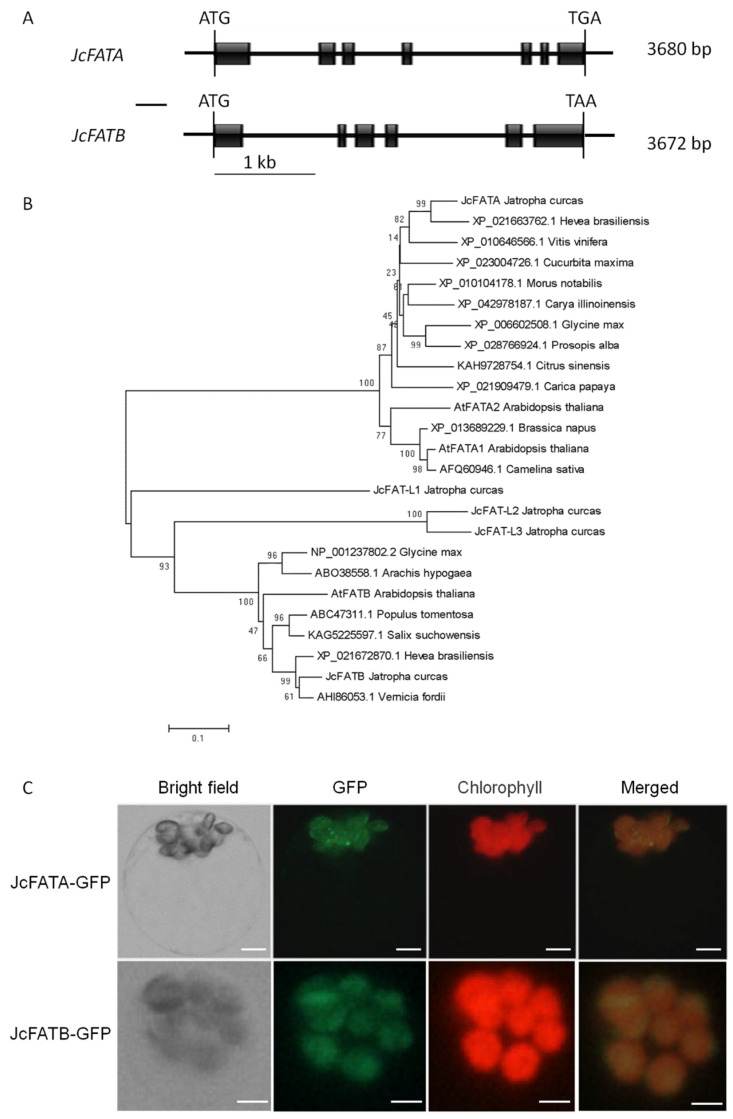
Figure 1.
Schemes of the JcFATA and JcFATB genes and characterization of the JcFATA and JcFATB proteins. (A) Genomic organization of the JcFATA and JcFATB genes. The closed black boxes indicate exons, and connecting lines indicate introns. The ATG start codon and TGA/TAA stop codon are also indicated. (B) Phylogenetic tree of JcFATA, JcFATB, and other FAT (fatty acyl-ACP thioesterase) proteins. The coding region sequences were aligned using Clustal W, and the evolutionary relationship was analyzed using the neighbor-joining method. Numbers on branches indicate the percentage of replicate trees in which the associated sequences clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates). The segment under the phylogenic tree is the evolutionary distance, which was computed using the Poisson correction method. The NCBI accession numbers for the FAT proteins of A. thaliana and J. curcas are presented in Table S1. (C) Subcellular localization of the JcFATA-GFP and JcFATB-GFP fusion protein in leaf protoplasts isolated from 8-day-old seedlings of wild-type A. thaliana Col-0. GFP, green fluorescent protein. Scale bars = 2 μm.