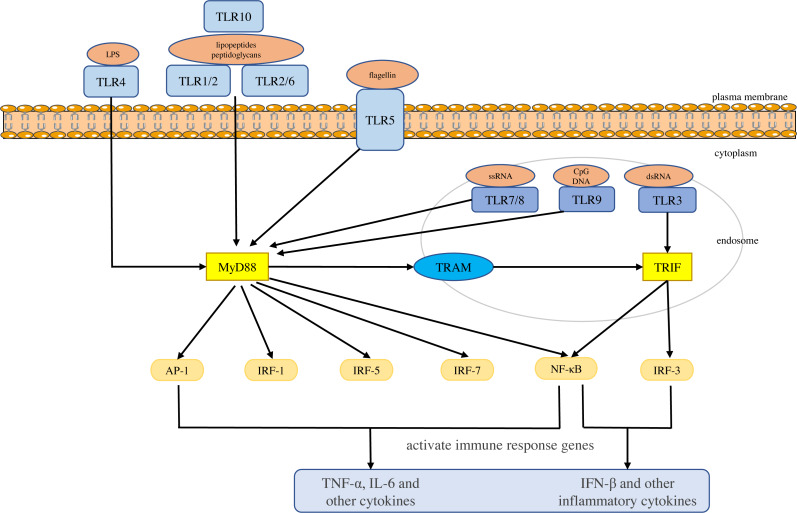
Figure 1. Toll-like receptor function and signal transduction.
The 10 toll-like receptors (TLRs) are divided into extracellular (TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6 and TLR10) and intracellular (TLR3, TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9) subtypes. Different components of microbial activate the extracellular TLRs and the intracellular TLR3, TLR7/TLR8, and TLR9 recognize viral dsRNA, ssRNA and unmethylated CpG DNA, respectively. MyD88 and TRIF are the two main junction pathways in TLR signal transduction. They transmit the signal downstream and activate immune response genes via transcription factors such as NF-κ B, AP-1, or IRF-1, IRF-3, IRF-5, and IRF-7 and induce the production of cytokines such as TNF-α and IFN-β.