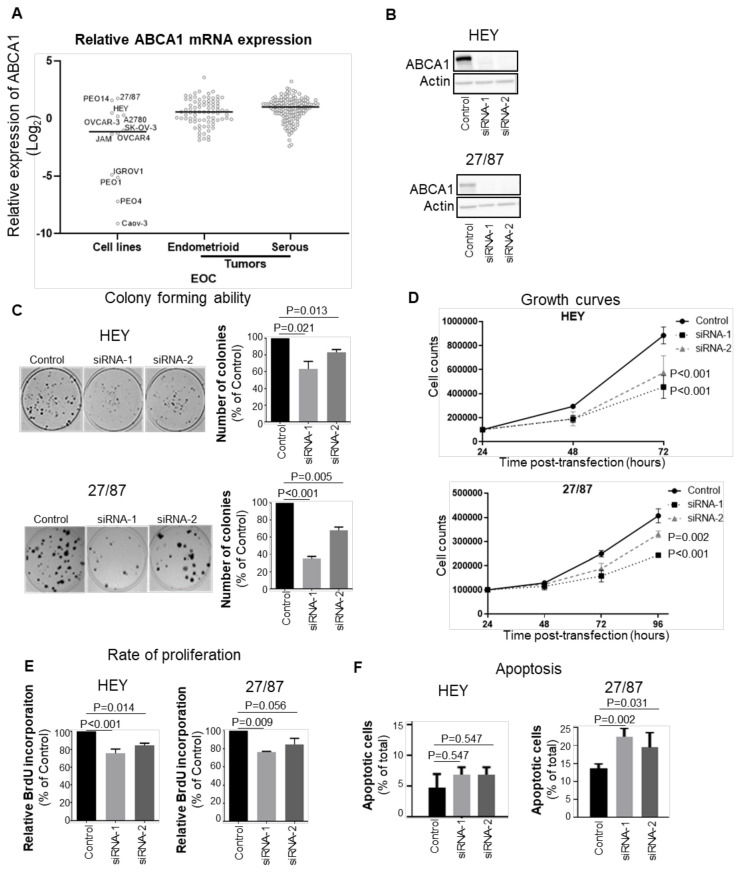
Figure 1.
ABCA1 is required for rapid growth of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) cells in monolayer. (A) RT-qPCR assessment of ABCA1 expression across a panel of cell lines and ovarian cancer tumours. ABCA1 mRNA expression was normalized to the control genes, GUSB and HPRT, and graphed relative to ABCA1 expression in PEO4. Black represents the median ABCA1 expression of the group. (B) Western blots showing the extent of the knockdown of ABCA1 by two independent siRNAs in the serous HEY and endometrioid 27/87 cell lines. (C) Suppression of ABCA1 impaired the colony forming ability of EOC cells. n = 3. p-Values were derived from one-sample t-tests. (D) ABCA1 knockdown reduced the growth of EOC cells, determined by cell counting. n ≥ 3. p-Values were derived from to-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests. (E) ABCA1 knockdown by siRNA-1 and siRNA-2 reduced the rate of EOC cell proliferation. n = 4 for HEY, n = 3 for 27/87. p-Values were derived from one-sample t-tests. (F) ABCA1 knockdown by siRNA-1 and siRNA-2 increased apoptosis in the 27/87 cells as measured by Annexin V and propidium iodide staining. n = 3. p-Values were derived from two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. All results represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD).