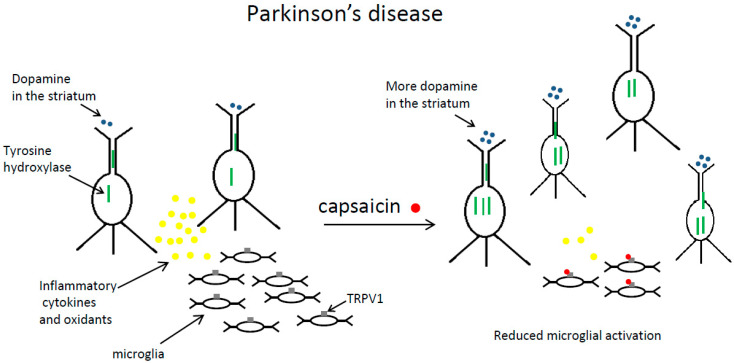
Figure 3.
The beneficial effects of capsaicin in Parkinson’s disease are shown in simplified form. Capsaicin administration increases the number of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the expression of tyrosine hydroxylase in these neurons. Consequently, there is more dopamine in the striatum. Moreover, after capsaicin treatment, microglial cells in the substantia nigra produce fewer oxidants and inflammatory cytokines. Left panel—before capsaicin treatment, right panel—after capsaicin treatment.