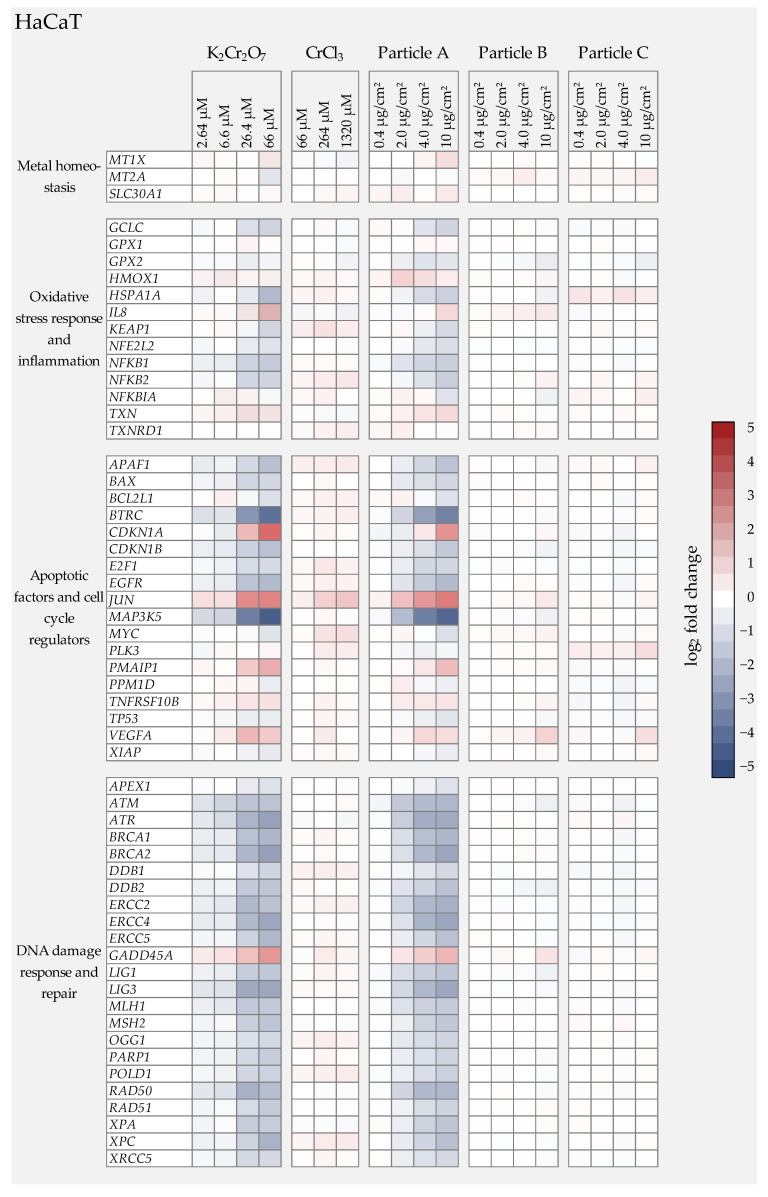
Figure 5.
Overview of the impact of K2Cr2O7, CrCl3, or three different Cr(III) oxide particles on human keratinocytes (HaCaT) using a high-throughput RT-qPCR approach with a custom-designed gene set. The genes under investigation have been clustered into groups associated with metal homeostasis, oxidative stress response, inflammation, apoptosis, and cell cycle regulation as well as DNA damage response and repair. HaCaT cells were treated with the respective chromium compound for 24 h. Displayed are the log2 fold changes of relative gene expression as a heatmap. Red colors indicate an enhanced expression, and blue colors indicate a down-regulation. The mean values of three independently conducted experiments are shown.