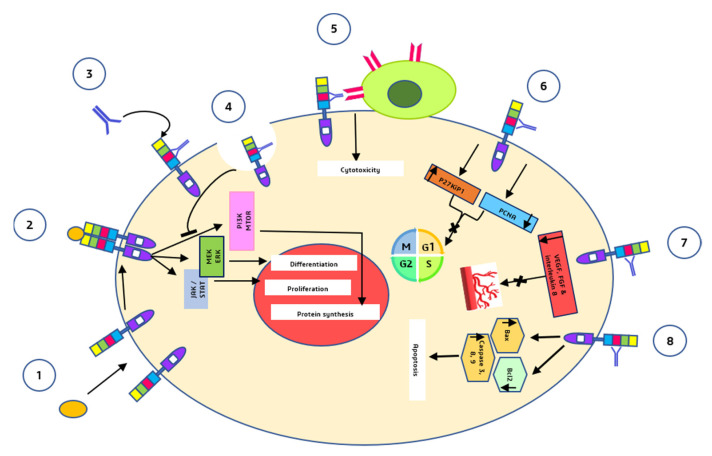
Figure 3.
Major anti-tumor mechanisms by which cetuximab acts (1) and (2) are the mechanisms that normally take place in the absence of cetuximab i.e., binding of the ligands to the EGFR monomers, induction of receptor dimerization, and downstream signalling pathways. (3) Cetuximab binds to domain III of EGFR. (4) Receptor internalization mediated by cetuximab and inhibition of downstream signalling pathways. (5) Fc segment of cetuximab binds to natural killer cells and induces ADCC. (6) G1 cell cycle arrest. (7) inhibition of angiogenesis. (8) Induction of apoptosis.