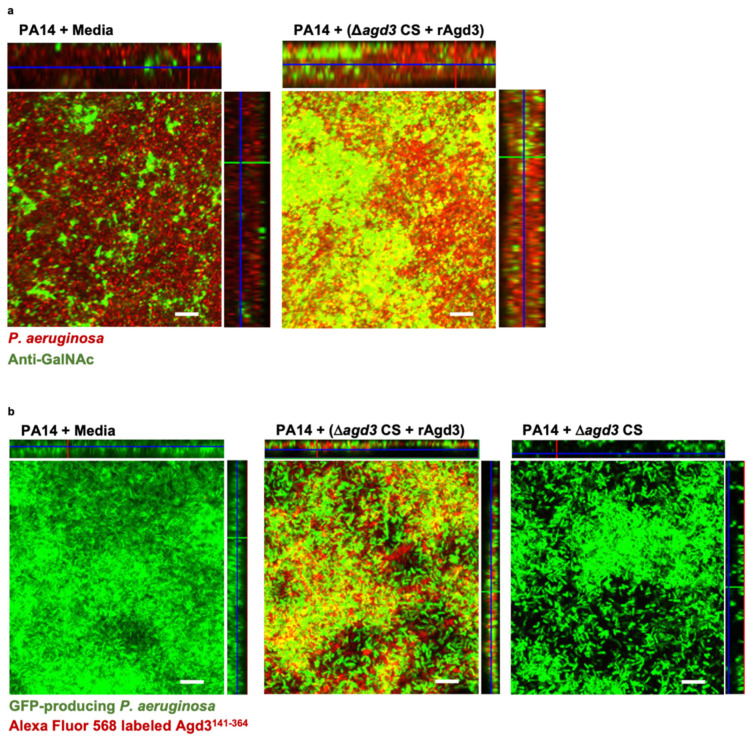
Figure 6.
GAG incorporates into P. aeruginosa biofilms. (a) Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy maximal intensity projections with orthogonal projections of wild-type P. aeruginosa (PA14) biofilms grown in the presence of de-N-acetylated GAG from a combination of N-acetylated GAG-containing culture supernatants and 165 nM recombinant Agd3 deacetylase (Δagd3 CS + rAgd3) or media. Exopolysaccharide was detected by staining with anti-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine antibody (anti-GalNAc) and an Alexa Flour-488 conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody (green). P. aeruginosa was counter stained with DRAQ5 (red). (b) Confocal microscopy maximal intensity projections with orthogonal projections of wild-type green fluorescent protein (GFP)-producing (green) P. aeruginosa (PA14) biofilms grown in the presence of de-N-acetylated GAG from a combination of Δagd3 CS and 165 nM rAgd3, Δagd3 CS alone or in media. Biofilms were imaged with fluorescence microscopy. Exopolysaccharide was detected by staining with Alexa Flour-568-labeled recombinant carbohydrate binding module Agd3141-364 (red). Representative images of 3 independent experiments. Biofilms were imaged at 630× (scale bar, 10 μm).