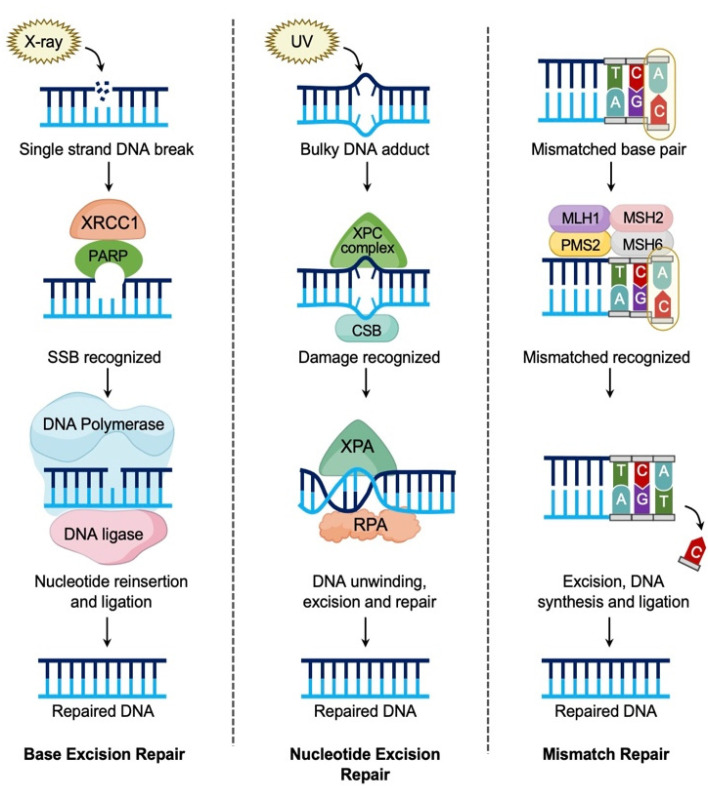
Figure 1.
Pathways of DNA repair- single strand DNA breaks. There are three pathways for correction of single strand DNA (ssDNA) breaks. Base excision repair: A single nucleotide base is missing due to spontaneous hydrolysis after DNA damage. XRCC1 and PARP with APE1 endonucleases recognize the damaged site and PARP-mediated repair is initiated. XRCC1 creates a scaffold for DNA polymerase and DNA ligase 3 which reinsert the base and ligate to repair the DNA strand. Nucleotide excision repair: A bulky DNA adduct is generated by environmental carcinogens such as ultraviolet (UV) light. The lesion is detected by xeroderma pigmentosa C complex (XPC complex) and Cockayne syndrome B (CSB) is recruited to the site. The DNA is unwound and XPA and replication protein A (RPA) stabilize the DNA for subsequent proteins to excise, synthesize, and complete the repair. Mismatch Repair: Errors during DNA replication can lead to mismatched base pairs. These mismatches are recognized by MSH2 and MSH6. MLH1 and PMS2 are then recruited to mismatch sites. The incorrect base is excised, replaced, and the corrected strand is ligated.