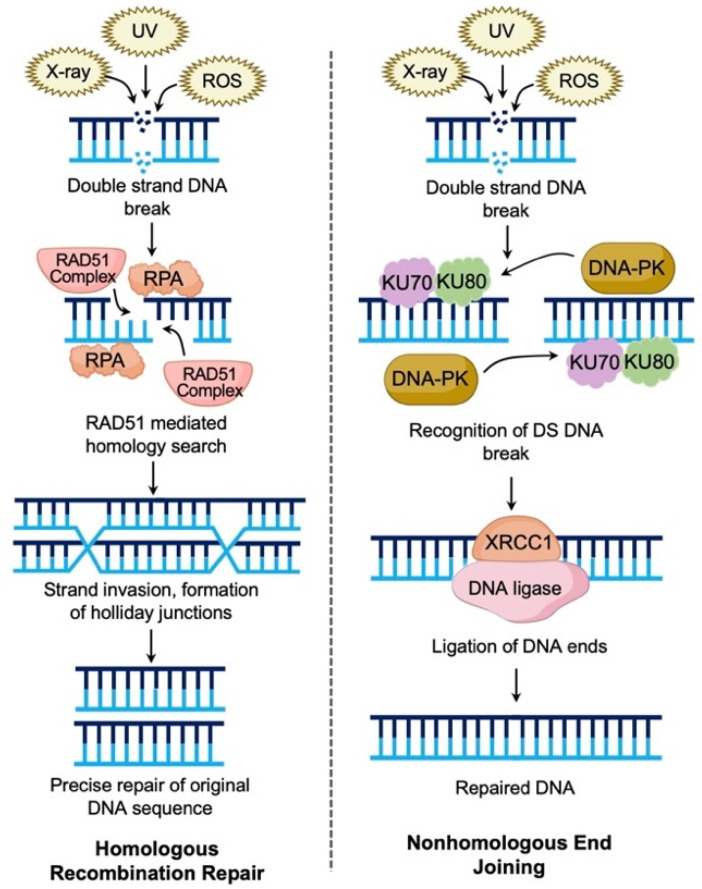
Figure 2.
Pathways of DNA repair- double strand DNA breaks. Double strand DNA (dsDNA) breaks can be caused by several exogenous and endogenous factors including radiation, UV rays, chemotherapeutic agents, and reactive oxygen species (ROS). There are two pathways for repair of dsDNA breaks. Homologous recombination repair: The dsDNA break is recognized. Exonuclease activity creates single-strand overhangs that are coated with RPA. The RAD51 complex composed of (RAD52 and BRCA2 proteins) initiate homology search and strand invasion. DNA is synthesized using the sister chromatid as a guide and creating double Holliday junctions. Resolving enzymes correct the junctions creating precisely repaired DNA. Nonhomologous end joining: The dsDNA break is recognized by the Ku-70-Ku80 heterodimer. This recruits DNA protein kinase (DNA-PK). The DNA ends are then ligated together after recruitment of XRCC4 and DNA ligase 4.