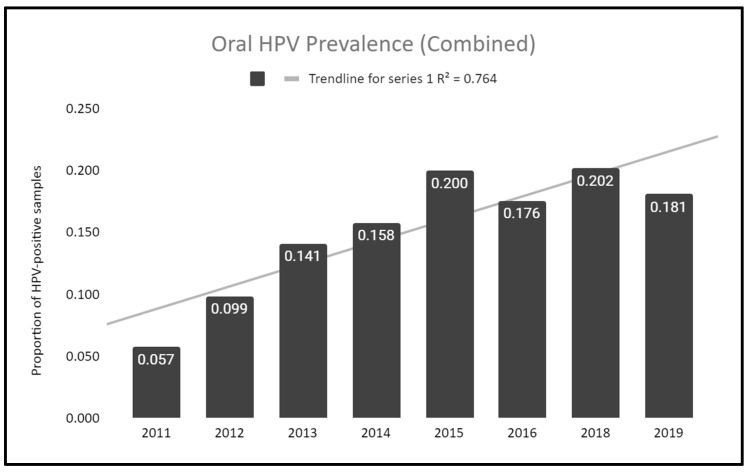
Figure 1.
Change in prevalence of high-risk oral HPV over time. Analysis of both pediatric and adult patients revealed an increase in high-risk HPV of 3.17-fold from 5.7% in 2011 to 18.1% in 2019, with the coefficient of determination or R2 = 0.764, suggesting a strong, positive correlation between more recent sample years and HPV-positive results.