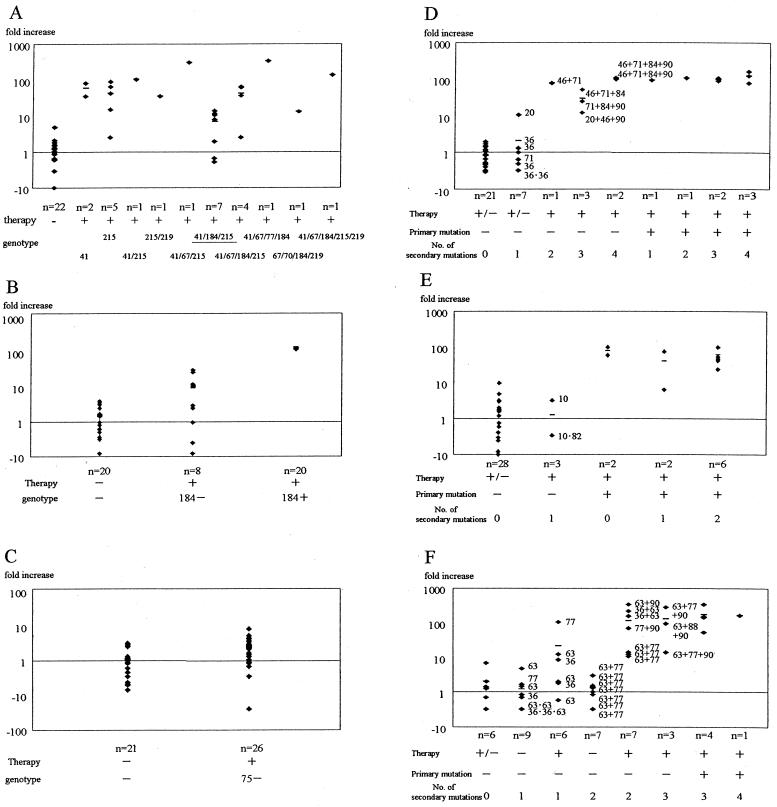
FIG. 1.
Relationship between resistance to AZT (A), 3TC (B), d4T (C), RTV (D), SQV (E), and NFV (F) and viral phenotype and genotype. The abscissas represent the genotypes of clinical isolates; n, number of isolates. The genotype numbers listed in panels A to C indicate the mutation sites of amino acids that confer drug resistance. Each numbers adjacent to a symbol in panels D to F indicates the mutation site of an amino acid that conferred drug resistance. Therapy, history of therapy using the respective drug. Phenotypic resistance is expressed as fold increase on the ordinate. The fold increase was calculated by dividing the IC50 of each drug by the mean IC50 for NL432 in each assay. The small horizontal bars represent the mean fold increase for each genotype. Some viruses with mutations at the sites underlined in panel A were AZT susceptible. +, present; −, absent; +/−, both treated and naive cases are included.