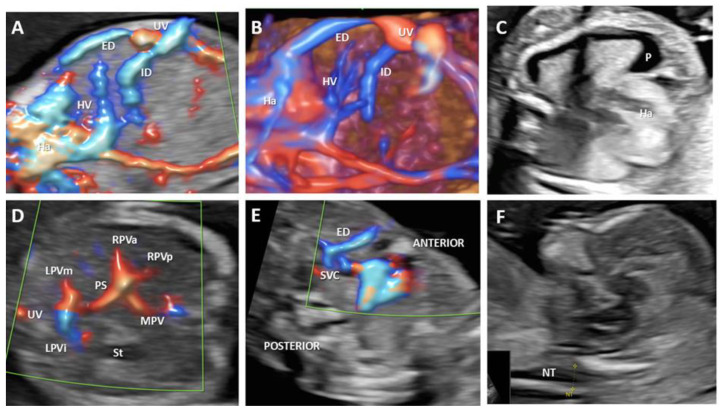
Figure 6.
Agenesis of the ductus venosus with complex drainage of the umbilical vein: intrahepatic umbilico-portal drainage, and extrahepatic drainage, into the superior vena cava at 14 weeks of gestation (case 4). (A): Longitudinal plane of the fetal abdomen, color Doppler evaluation, showing the absence of ductus venosus and umbilical drainage. (B): 3D evaluation showing the abnormal umbilical vein drainage: umbilico-portal and into superior vena cava. (C): Transverse view at the thorax level showing the presence of pleural effusion. (D): Transverse view at the abdomen level showing a normal portal venous system (E): Three-vessel view showing the extrahepatic drainage of the umbilical vein into the superior vena cava. (F): Median section used for the sonographic measurement of nuchal translucency thickness. UV—umbilical vein. SVC—superior vena cava. ED—extrahepatic drainage. ID—intrahepatic drainage. HV—hepatic vein, Ha—the heart. P—pleural effusion. MPV—main portal vein. PS—portal sinus. RPVa—the anterior branch of the right portal vein. RPVp—the posterior branch of the right portal vein. LPVi—left portal vein inferior branch; LPVm—left portal vein medial branch. St—stomach. NT—nuchal translucency.