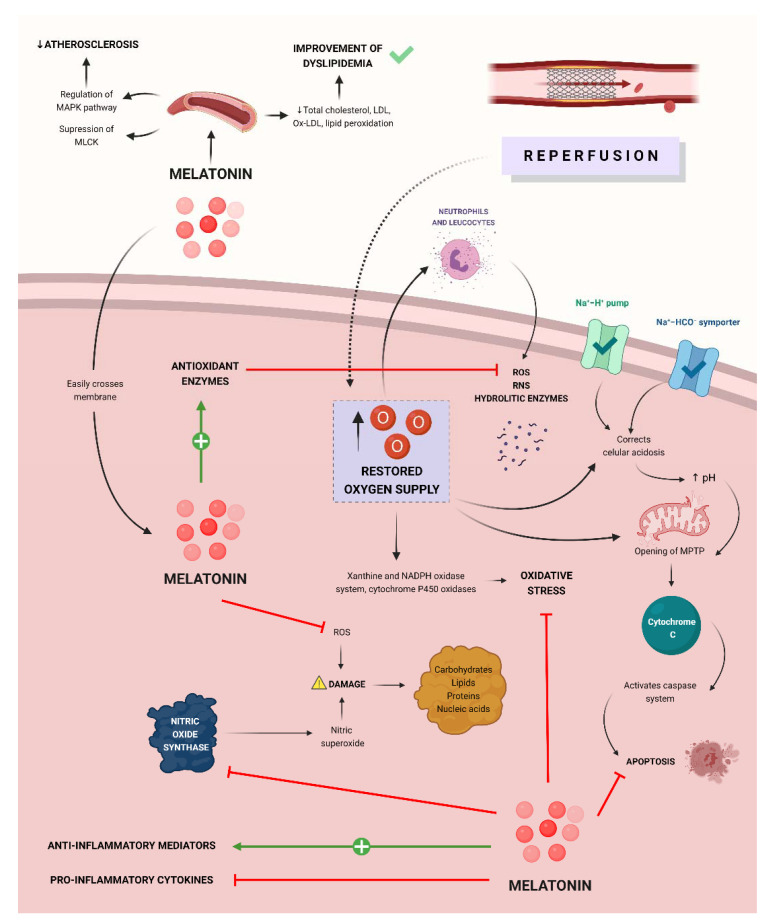
Figure 3.
Mechanisms through which melatonin exerts myocardial protection in MI/R injury. Melatonin is capable of inhibiting the nitric oxide synthase, pro-inflammatory cytokines, ROS, and cellular pathways conducting to apoptosis. It is also responsible for enhancing anti-inflammatory mediators and antioxidant enzymes. Extracellularly, melatonin decreases atherosclerosis and improves dyslipidemias, which reduce the risk of ischemic episodes.