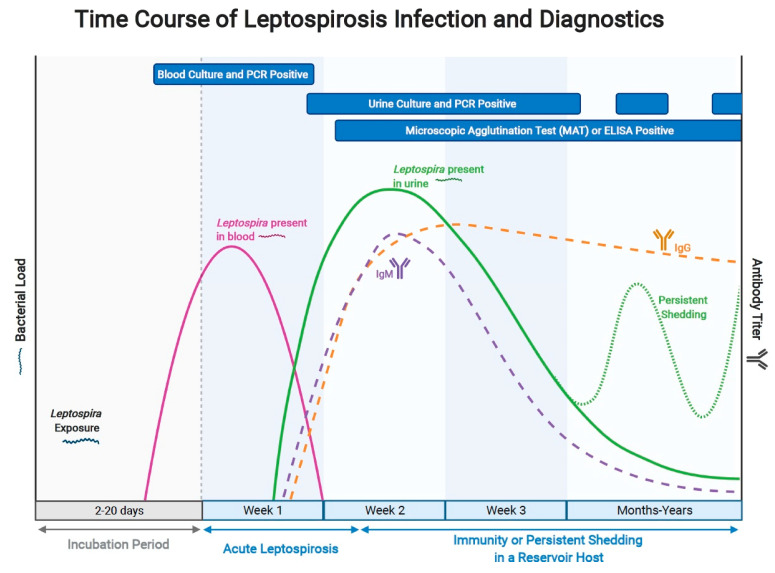
Figure 2.
Kinetics of leptospiral infection and corresponding diagnostic tools. Infection with Leptospira spp. results in leptospiremia 2–20 days after exposure and leptospiruria approximately one week later. In some hosts, persistent infection of the renal tubules leads to persistent or waxing and waning urinary shedding or organisms. Leptospira antibodies are produced after 1 week of infection and can persist for months to years. Bacterial culture or molecular detection of leptospiral DNA can be utilized when bacteria are likely to be present in the collected specimen depending on the course of disease. Antibody detection assays, including the microscopic agglutination test, are often negative in the first week of infection; therefore, paired sera collected during the acute phase and 1–2 weeks later are recommended. Adapted from “Time Course of COVID-19 Infection and Test Positivity”, by BioRender.com (2021). Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates (accessed 11 April 2021).