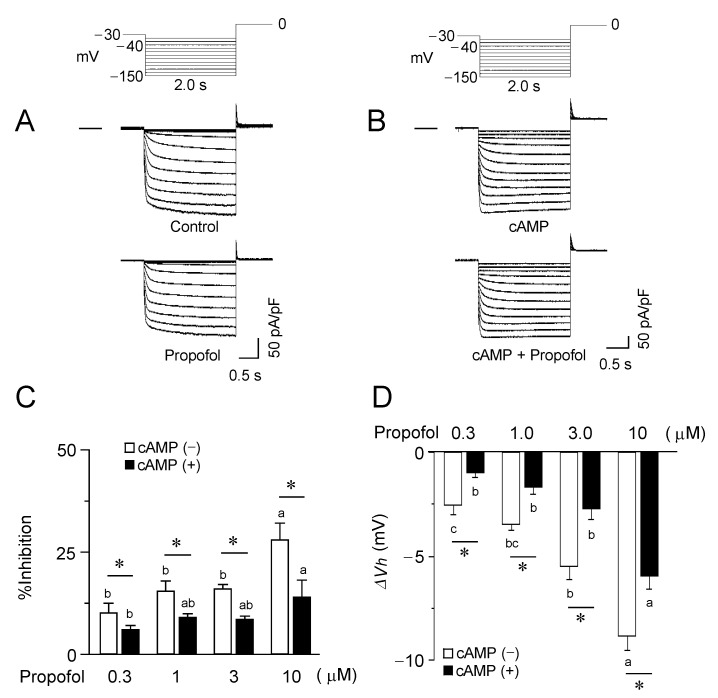
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effects of propofol on HCN2 channels. (A) Superimposed current traces from HCN2-expressing CHO cells, recorded using the above-mentioned pulse protocol, before (upper, control) and 2–3 min after exposure to propofol at 10 μΜ (lower). The horizontal line to the left of the current traces indicates zero level. (B) Current recordings in a cell preloaded with cAMP (50 μΜ) via pipette. The concentration of propofol is the same as A. (C) The percentage inhibition of the saturating current density at various concentrations of propofol in the presence and absence of cAMP. Data represent the mean ± S.E.M. *, p < 0.05. (D) Shifts in Vh caused by propofol at various concentrations in the presence and absence of cAMP. Bars represent the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 6). The different letters in (C,D) indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05 according to the Tukey’s multiple range test and t-test (* indicates the difference in the presence and absence of cAMP; a, b, c, indicate different propofol concentration.).