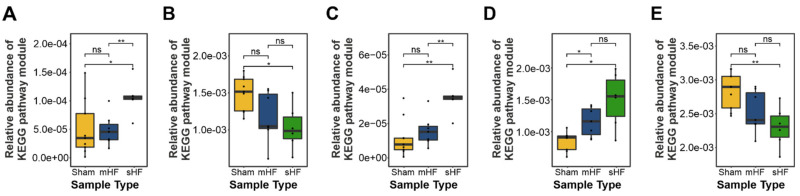
Figure 7.
Box plots showing the differentially abundant KEGG pathway modules for amino acid metabolism. (A) Branched-chain amino acid degradation-related genes in the sHF, mHF, and Sham samples (Kruskal–Wallis test p-value = 0.001). (B) Aromatic amino acid metabolism in the sHF, mHF, and Sham samples (Kruskal–Wallis test p-value = 0.024). (C) Aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in the sHF, mHF, and Sham samples (p-value = 0.012). (D) Positively charged amino acid degradation in the sHF, mHF, and Sham samples (Kruskal–Wallis test p-value = 0.036). (E) Positively charged amino acid biosynthesis in the sHF, mHF, and Sham samples (Kruskal–Wallis test p-value = 0.018). (n values are as follows: Sham = 9, mHF = 7, sHF = 6). * and ** correspond to p ≤ 0.05, p ≤ 0.01 respectively; ns, non-significant.