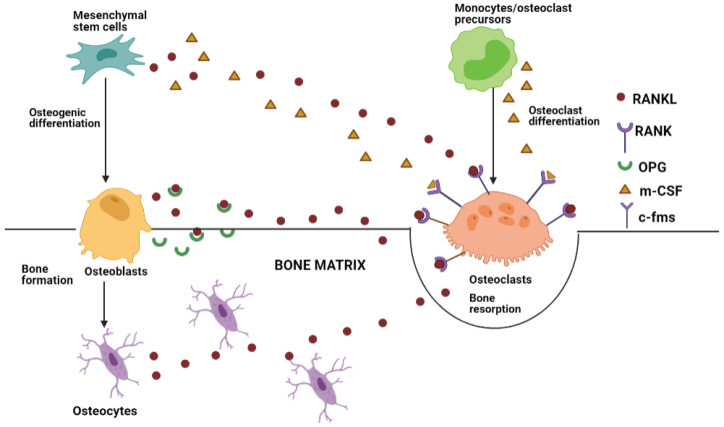
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of role of RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling in Bone homeostasis. Bone formation initiates with osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts. A sub population of these osteoblasts are terminally differentiated into osteocytes, which embed inside the bone matrix. Specific matrix sensing by the osteocytes triggers recruitment of osteoclast precursors (monocytes/macrophages), which differentiate into osteoclasts. During early osteoclast differentiation, MSCs and the precursor cells secrete M-CSF, which binds to c-fms receptor on the osteoclasts. This process is also coupled with release of RANKL from MSCs, osteoblasts, and osteocytes, which binds to RANK receptor on osteoclasts. Additionally, osteoblasts also secrete OPG inhibitor for competitive inhibition of RANKL to counter the bone resorption process.