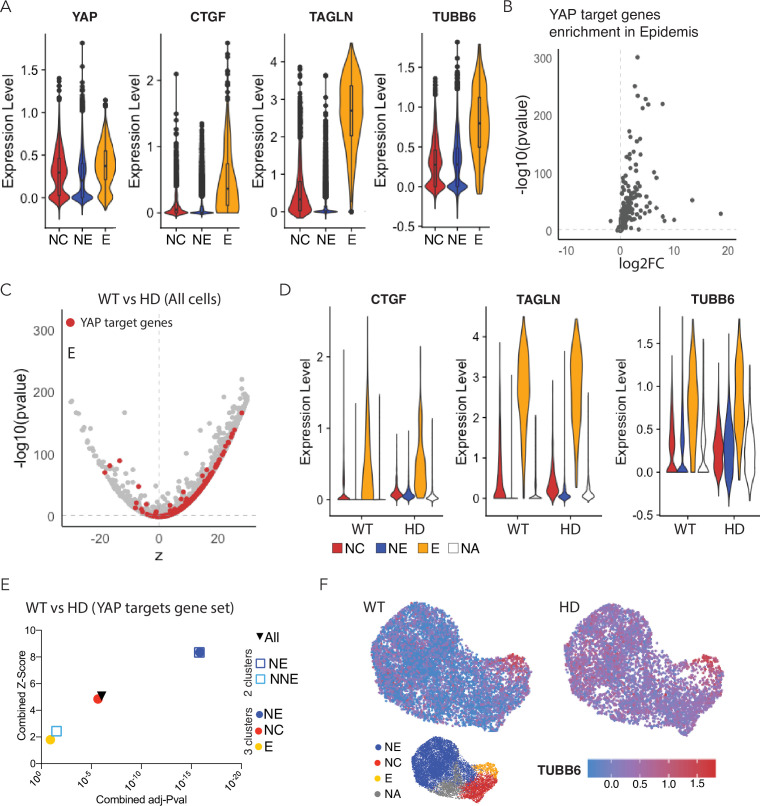
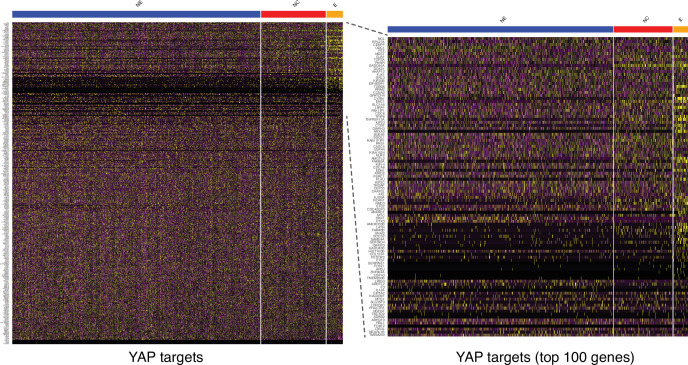
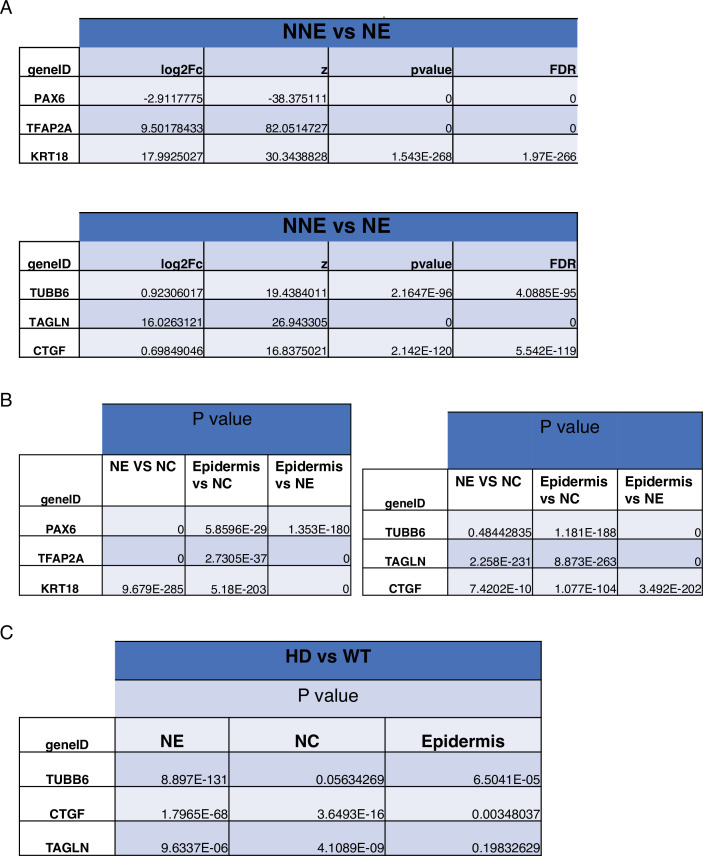
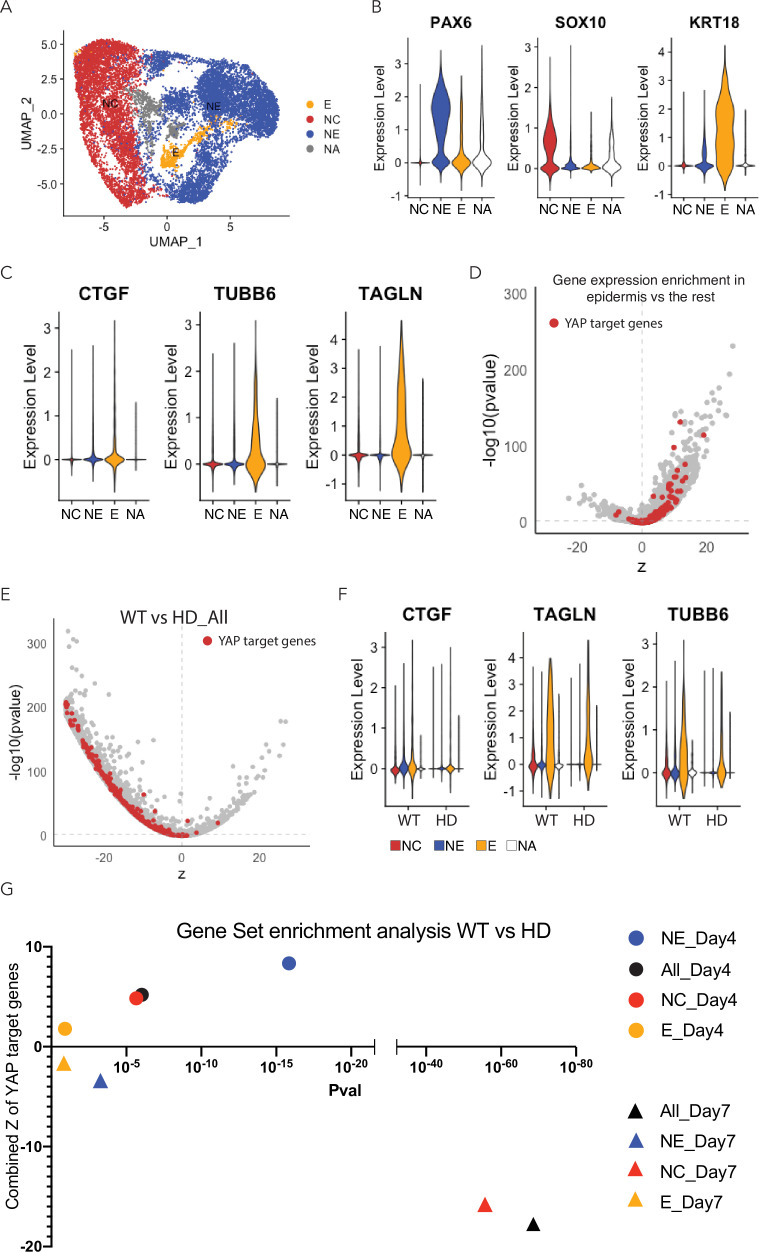
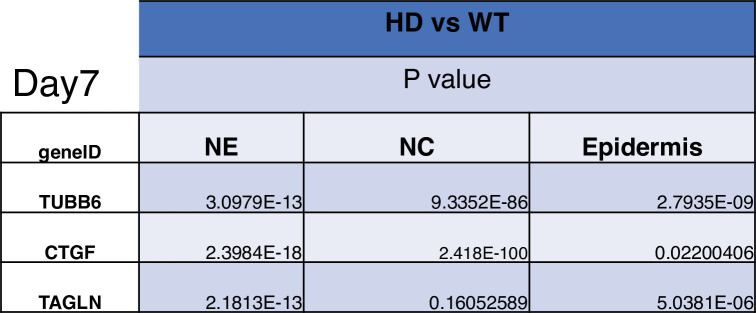
Figure 5. Expression of YAP target genes in WT and HD neuruloids.
(A) Violin plots show the expression of YAP and three representative target genes in the three clusters representing the main ectodermal lineages from scRNA-seq analysis of D4 neuruloids. Expression levels are normalized counts, calculated by Seurat for each gene and plotted on a logarithmic scale. (B) A volcano plot shows the greater expression of several YAP target genes in epidermis compared to the remainder of the neuruloid. (C) An analysis of differential gene expression from scRNA-seq data shows upregulation of YAP target genes (red) in HD with respect to WT neuruloids. (D) Violin plots show the expression of three representative YAP target genes in the three lineage clusters from D4 WT and HD neuruloids. The color code is: neural crest (NC), red; neural ectoderm (NE), blue; epidermis (E), yellow; and unidentified (NA), white. The augmented expression of YAP target genes is more pronounced in the nonepidermal lineages. (E) Gene-set enrichment analysis of YAP target genes confirms the effect. (F) Analysis by uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) shows the ectopic enhancement of a representative YAP target, TUBB6, in D4 WT and HD neuruloids. Full statistics are provided in Figure 5—figure supplement 5. HD, Huntington’s Disease.