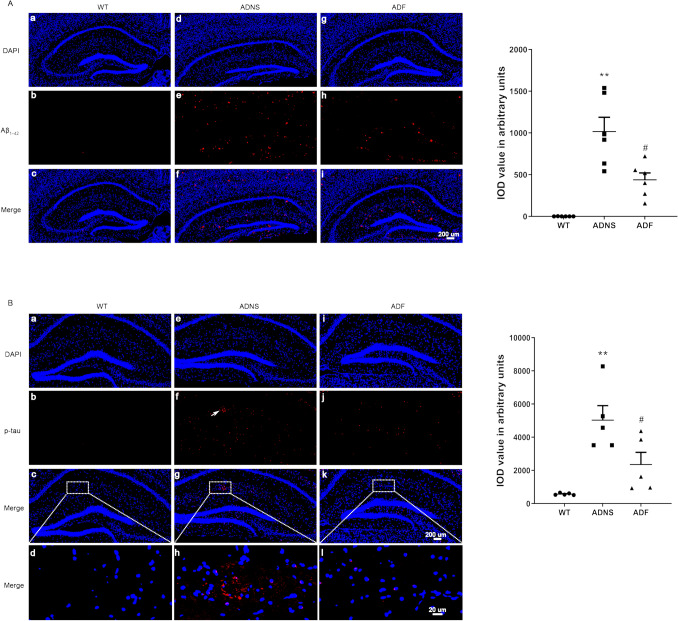
Figure 1.
Fasudil treatment reduced Aβ plaque deposition and phosphorylated tau tangles in the hippocampus. (A) Aβ1-42 plaques was checked in the hippocampus of the mice in each group. (a–c) WT, (d–f) ADNS, (g–i) ADF. Immunofluorescent intensity quantification of anti-Aβ1-42 showed significant increased intensity in ADNS group when compared with WT (p < 0.01) and the reverse in the Fasudil-treated mice, suggesting the protective effect on Aβ burden and therapeutic potential for clearance of Aβ plaques in AD with Fasudil treatment. (B) Tau phosphorylation at S404 was checked in the hippocampus of the mice in each group. (a–d) WT group, (e–h) ADNS group, (i–l) ADF group. Images (a–c, e–h, i–l) were taken at 10× (200 μm). The box area is enlarged, and the images (d, h, l) were taken at 60× (20 μm). DAPI (blue) was used for nuclei staining. Immunofluorescent intensity quantification of anti-Phospho-Tau (S404) showed a significant increase in intensity in the ADNS group when compared with WT (p < 0.01); the reverse was observed in the Fasudil-treated mice. Data is presented as Mean ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus WT; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 versus ADNS. The Dunnett’s test were used for statistical analysis.