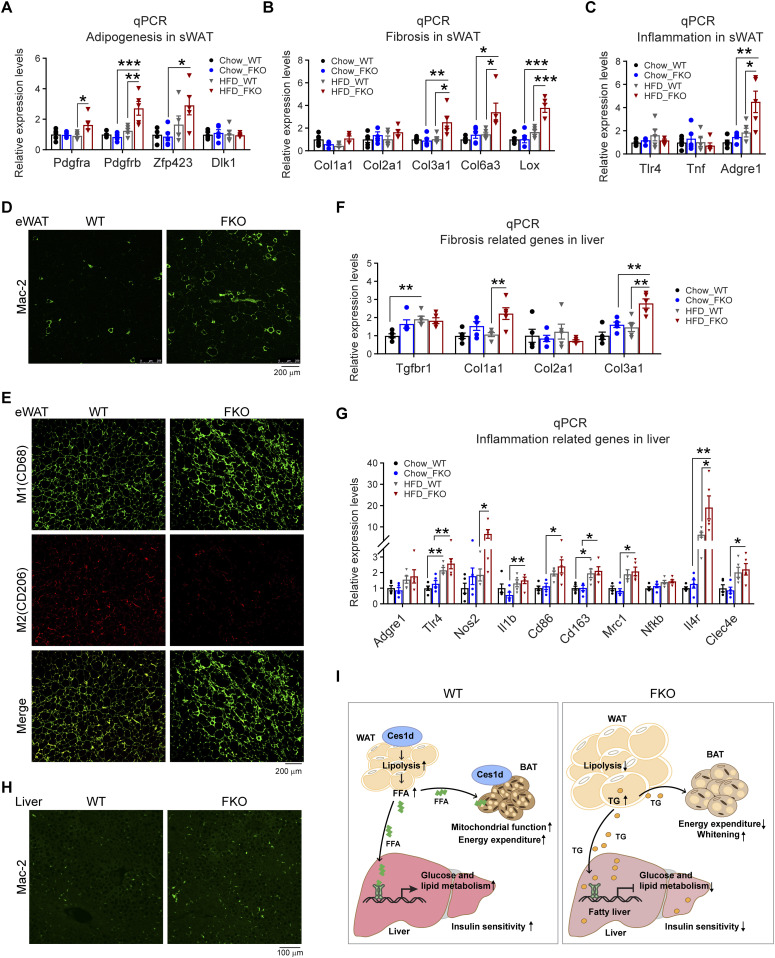
Figure 11. Deficiency of Ces1d in adipose tissue causes local unhealthy microenvironment in adipose tissue and the liver, ultimately leading to systemic insulin resistance.
(A) qPCR analysis for the mRNA levels of adipogenesis-related genes including Pdgfa, Pdgfb, Zfp243, and Dlk1 in the sWAT of WT and FKO mice fed on regular chow or HFD (n = 5 in each group, each point represents a biology replicate, representative of three repeats). Data are represented as mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (B) qPCR analysis for the mRNA levels of fibrosis related genes including Col1a1, Col2a1, Clo3a1, Clo6a3, and Lox in the sWAT from WT and FKO mice fed on regular chow or HFD (n = 5 in each group, each point represents a biology replicate, representative of three repeats). Data are represented as mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C) qPCR analysis for the mRNA levels of inflammation related genes including Tlr4, Tnf, and Adgre1 in the sWAT of WT and FKO mice fed on regular chow or HFD (n = 5 in each group, each point represents a biology replicate, representative of three repeats). Data are represented as mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (D) IF staining with α-Mac-2 antibody on the eWAT of WT and FKO mice fed on HFD (representative of six fields, experiments were repeated for three times; scale bars: 200 μm). (E) Co-IF staining with α-CD68 (green) and α-CD206 (red) antibodies on the eWAT of WT and FKO mice fed on HFD (representative of six fields, experiments were repeated for three times; scale bars: 200 μm). (F) qPCR analysis for the mRNA levels of fibrosis related genes including Tgfbr1, Col1a1, Col2a1, and Col3a1 in the liver from WT and FKO mice fed on regular chow or HFD (n = 5 in each group, each point represents a biology replicate, representative of three repeats). Data are represented as mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA, **P < 0.01. (G) qPCR analysis for the mRNA levels of inflammation related genes including Adgre1, Tlr4, Nos2, Il1b, Cd86, Cd163, Cd206, Nfkb, Il-4r, and Clec4e in the liver of WT and FKO mice fed on regular chow or HFD (n = 5 in each group, each point represents a biology replicate, representative of three repeats). Data are represented as mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (H) IF staining with α-Mac-2 antibody on the liver of WT and FKO mice fed on HFD (representative of six fields, experiments were repeated for three times, scale bars: 100 μm). (I) Left: In the normal adipose tissue, Ces1d hydrolyzes the lipid droplet TG. The produced FFAs circulate into BAT and the liver where they serve as the substrates for energy generation. Moreover, the FFAs also function as signaling molecules to activate the lipid-sensing transcriptional factors to regulate the glucose and lipid metabolic homeostasis. Right: In the Ces1d-deficient adipose tissue, insufficiency of lipolysis leads to the formation of larger lipid droplets in adipocytes. The excessive nutritional stress, especially under HFD challenging condition may cause increased ectopic deposition of TG in peripheral tissues. This leads to lipotoxicity, which further induces fatty liver and whitening of the BAT. Concomitantly, absence of the key signaling FFAs might blunt the proper regulations of key metabolic genes, which further worsens the metabolic adverse effects. Ultimately, the mice develop whole-body insulin resistance.