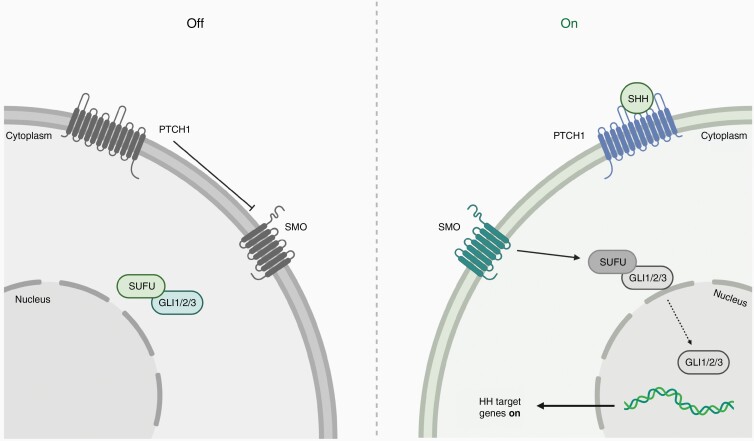
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the SHH signaling pathway. In inactivated status PTCH1 inhibits SMO and SUFU is bound to GLI1, GLI2 or GLI3 in cytoplasm (left panel); if SHH (ligand) binds to PTCH1 transmembranal SMO gets activated; GLI1/2/3 is released and translocted to nucleus where it functions as transcription factor (right panel); Adapted from “Hedgehog Signaling Pathway”, by BioRender.com (2021). Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates.