Fig. 10.
HFOs (>250 Hz) are frequent interictally, before and during seizures, and are recorded primarily from the IHKA injection site
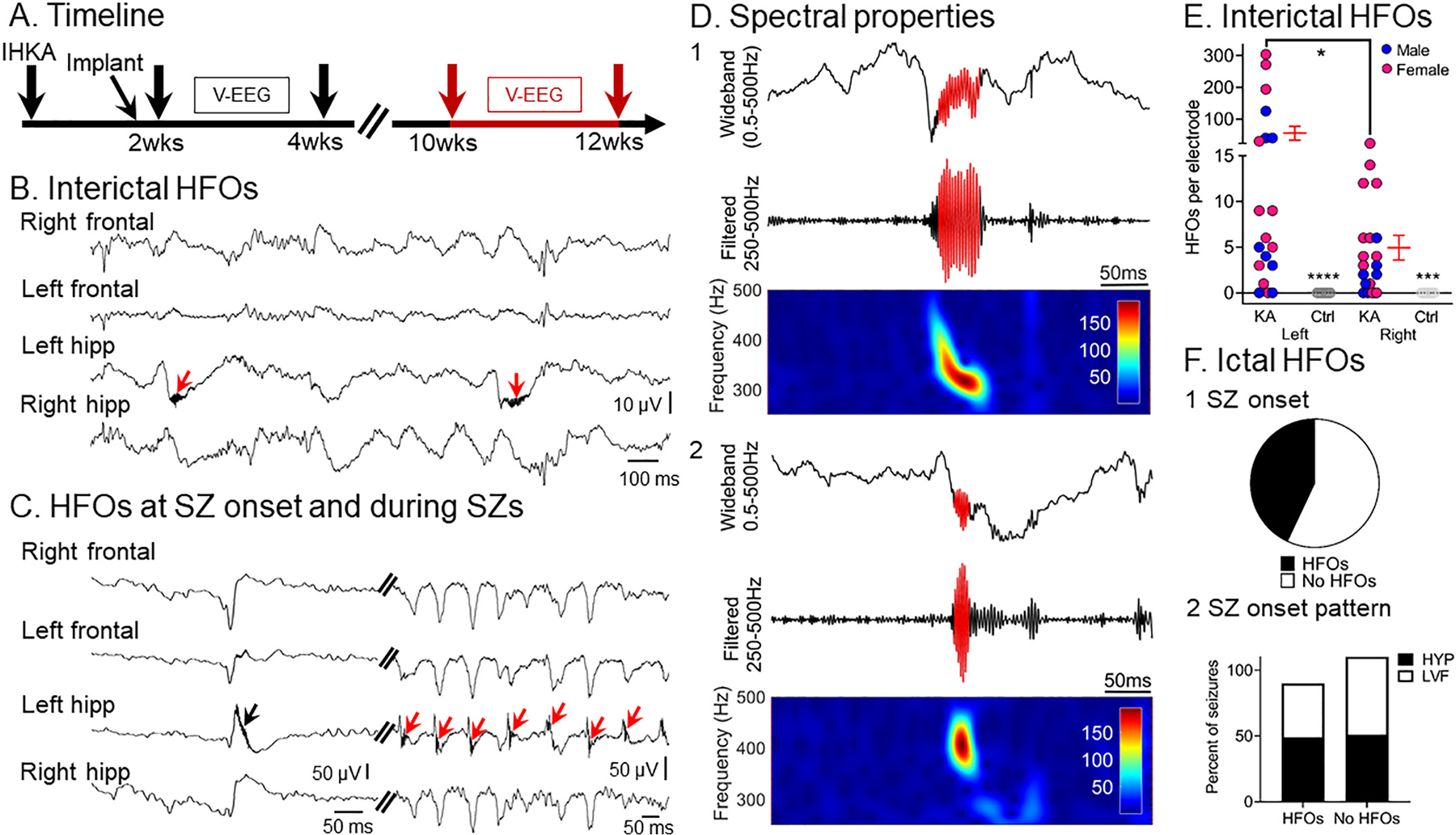
(A) Experimental timeline of the study. The data used for this figure come from the 10–12 wk timepoint (red arrows).
(B) Representative example of interictal HFOs recorded from the left hemisphere. Note the presence of HFOs (red arrows) in the left hippocampal lead where they were in the trough of slow waves. Note that interictal HFOs were not always in the trough of slow waves, however.
(C) An example of an HFO recorded at the sentinel spike of an LVF seizure (black arrow) as well as during the seizure (red arrows). In this instance, HFOs were primarily recorded from the left hippocampal lead but this was not always the case.
(D) Two examples of HFOs (D1, D2). For both D1 and D2, the top is wideband recording (0.5–500 Hz) showing coupling of HFOs to the trough of slow waves. The centers are the filtered traces (250–500 Hz) and the bottom shows spectral properties of HFOs with frequencies >250 Hz in the 250–500 Hz time-frequency domain.
(E) Quantification of HFOs (events/min) based on either the left (hippocampus or cortex) or right (hippocampus or cortex) electrodes for IHKA and Saline-injected animals. HFOs were more frequent in the left hemisphere compared to the right (Wilcoxon signed rank test, p = 0.01). HFOs were not detected in controls. Comparisons of IHKA- and Saline-injected mice showed increased HFOs in IHKA-injected mice for both left and right electrodes (Left: Mann-Whitney U test, U = 18, p < 0.0001, Right: Mann-Whitney U test, U = 30, p < 0.0001). Blue and pink represent males and females, respectively. Data are presented as individual values and as mean ± SEM (red).
(F) The percent of seizures that showed HFOs at their onset (F1). The percentage of HYP vs. LVF seizures that showed HFOs at seizure onset was not statistically different (Fisher’s exact test, p > 0.05; F2). The percentage of HYP and LVF seizures for each category (HFOs, no HFOs) was calculated for the total number of seizures for each seizure type (HYP or LVF).
