Fig. 7.
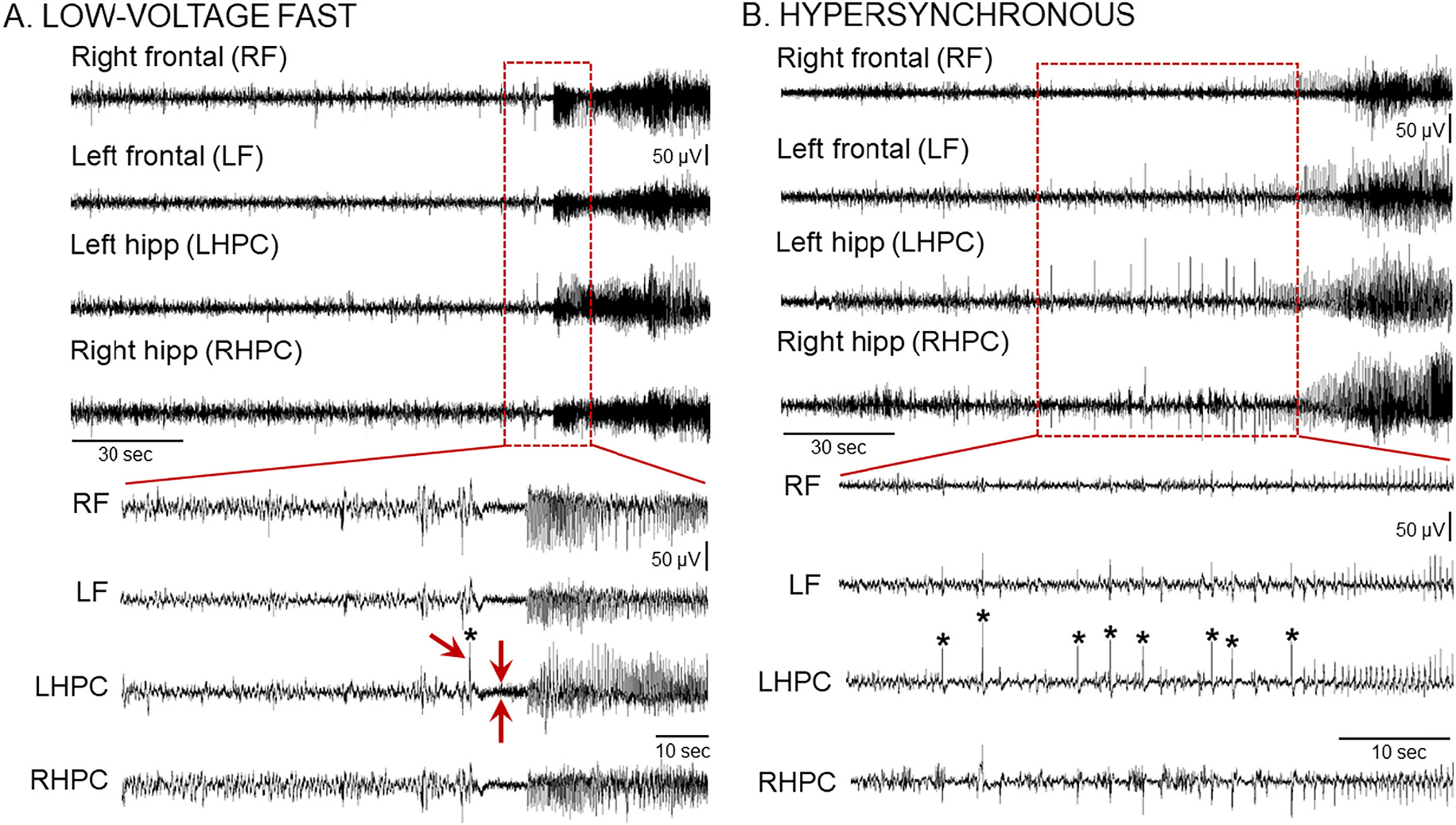
Chronic IHKA seizures show different seizure onset patterns
(A) Representative example of a low-voltage fast (LVF) onset seizure recorded during the 10–12 wk recording session post-IHKA. A 30 s-long EEG trace (Top) and an expanded 10 s-long epoch (Bottom) taken from the seizure onset are shown. Note that the LVF pattern starts with a sentinel spike (asterisk and single red arrow in the expanded trace at the Bottom) followed by brief suppression of the background EEG (2 red arrows pointing at each side of the EEG suppression) and subsequent series of spikes. Additional examples of LVF seizures are shown in Supplemental Fig. 7.
(B) Representative example of a hypersynchronous (HYP) onset seizure recorded during the 2–4 wk recording period post-IHKA. A 2 min-long EEG trace (Top) and an expanded 30 s-long epoch (Bottom) taken from the seizure onset are shown. Note that the HYP patterns start with a series of spikes (asterisks) followed by spikes at increased frequency. Additional examples of HYP seizures are shown in Supplemental Fig. 8.
