Fig. 9.
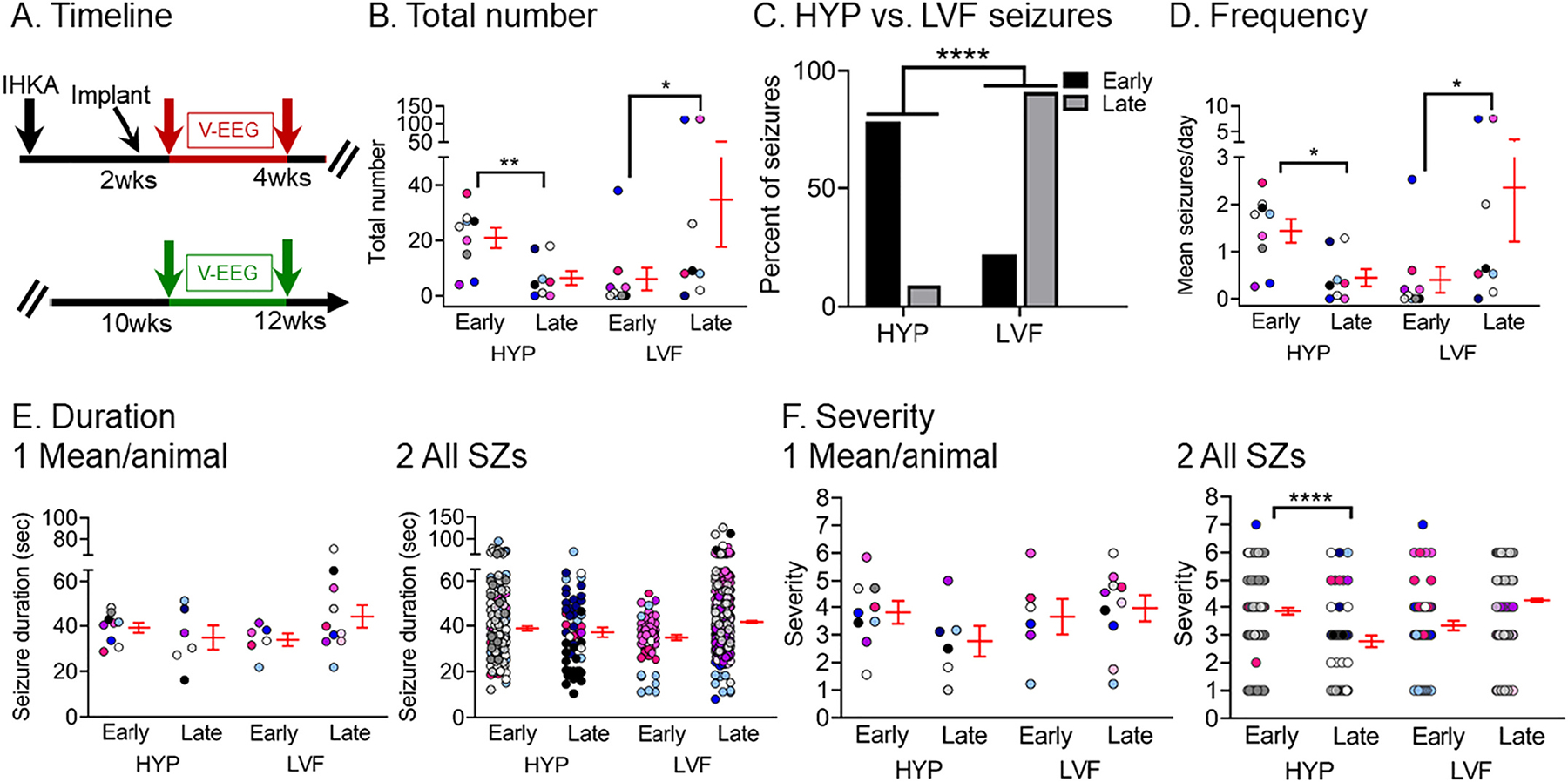
Quantification of different seizure onset patterns between timepoints
(A) Experimental timeline of the study. The data used for this figure were both from the 2–4 wk (red arrows) and 10–12 wk timepoint (green arrows). Seizures were distinguished as HYP or LVF. Seizures that were unclear in onset are not included in this figure because they were relatively rare (see Fig. 8).
(B) The total number of chronic HYP and LVF seizures recorded at the early (2–4 wks) and late (10–12 wks) timepoints are shown. HYP seizures were more frequent early whereas LVF seizures were more frequent late (HYP: paired t-test, tcrit = 5.63, p = 0.0013; LVF: Wilcoxon signed rank test, p = 0.04; Fig. 9B). In B and D–F, data are presented as individual values and as mean ± SEM (red).
(C) The percent of HYP vs. LVF seizures are shown for early and late timepoints. The percentage for each seizure category is shown for each timepoint. HYP seizures dominated early timepoints whereas LVF seizures dominated late timepoints (Fisher’s exact test, p < 0.0001).
(D) HYP and LVF seizure frequency was calculated as the mean number of seizures per day for each timepoint (early, late). HYP seizures were more frequent early vs. late (Wilcoxon signed rank test, p = 0.01), whereas LVF seizures were more frequent late vs. early (Wilcoxon signed rank test, p = 0.01).
(E) HYP and LVF seizure duration was calculated as the mean number of seizures per day for each animal at each timepoint (early, late; E1). No significant differences were found (Wilcoxon signed rank test, p > 0.05). (E2) Same as in E1 but all HYP and LVF seizures were pooled and are presented according to timepoint and type (HYP, LVF). No significant differences were found (Wilcoxon signed rank test, p > 0.05).
(F) HYP and LVF seizure severity was calculated as the mean per animal at each timepoint (early, late; F1). (F2) Same as in F1 but all seizures were pooled and are presented according to timepoint and type (HYP, LVF). HYP early seizures were less severe than HYP late seizures (Wilcoxon signed rank test, p < 0.0001).
