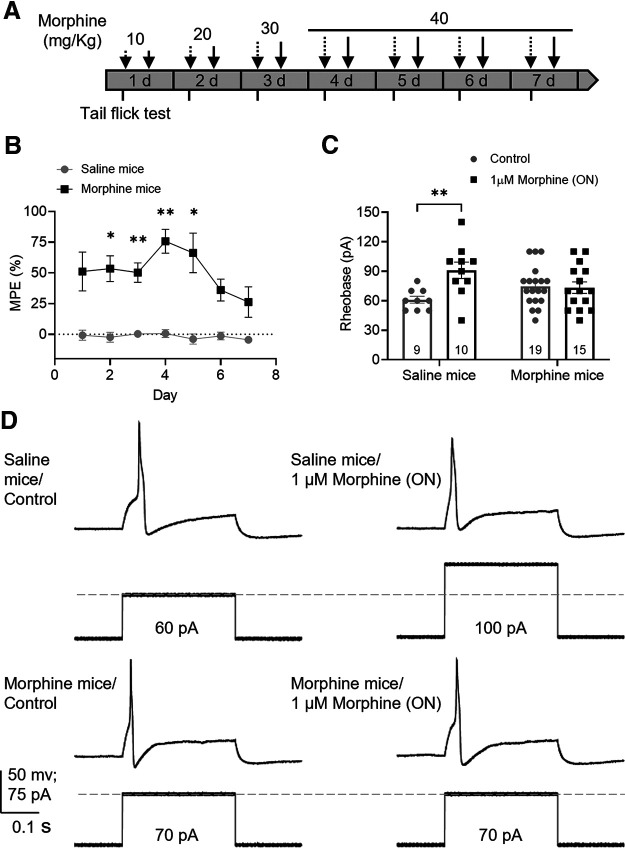
Figure 1.
Chronic morphine treatment induces tolerance in mouse DRG neurons. A, Schematic protocol of chronic morphine treatment. Dashed arrows indicate morning i.p. injections. Solid arrows indicate afternoon i.p. injections. Tail-flick assay (short ticks) was performed before and after morning injections. B, In vivo tail-flick test showed that morphine had an antinociceptive effect compared with saline (F(1,10) = 117.5, p < 0.0001, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test); this effect declined after day 4 despite high doses suggesting OT. Results are expressed as the mean of % MPE ± SEM, saline mice = 6; morphine mice = 6. C, Effect of overnight 1 μm morphine on rheobase of DRG neurons measured by patch clamp from saline and morphine-treated mice shows tolerance to morphine in neurons from morphine-treated mice (F(1,49) = 5.57, p = 0.022, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test). Number of cells appears in each bar. *p ≤ 0.05. **p ≤ 0.01. D, Representative recordings of the rheobase (minimal current to elicit an action potential) of DRG neurons from saline and morphine-treated mice exposed to vehicle (control) or morphine overnight.