Figure 3.
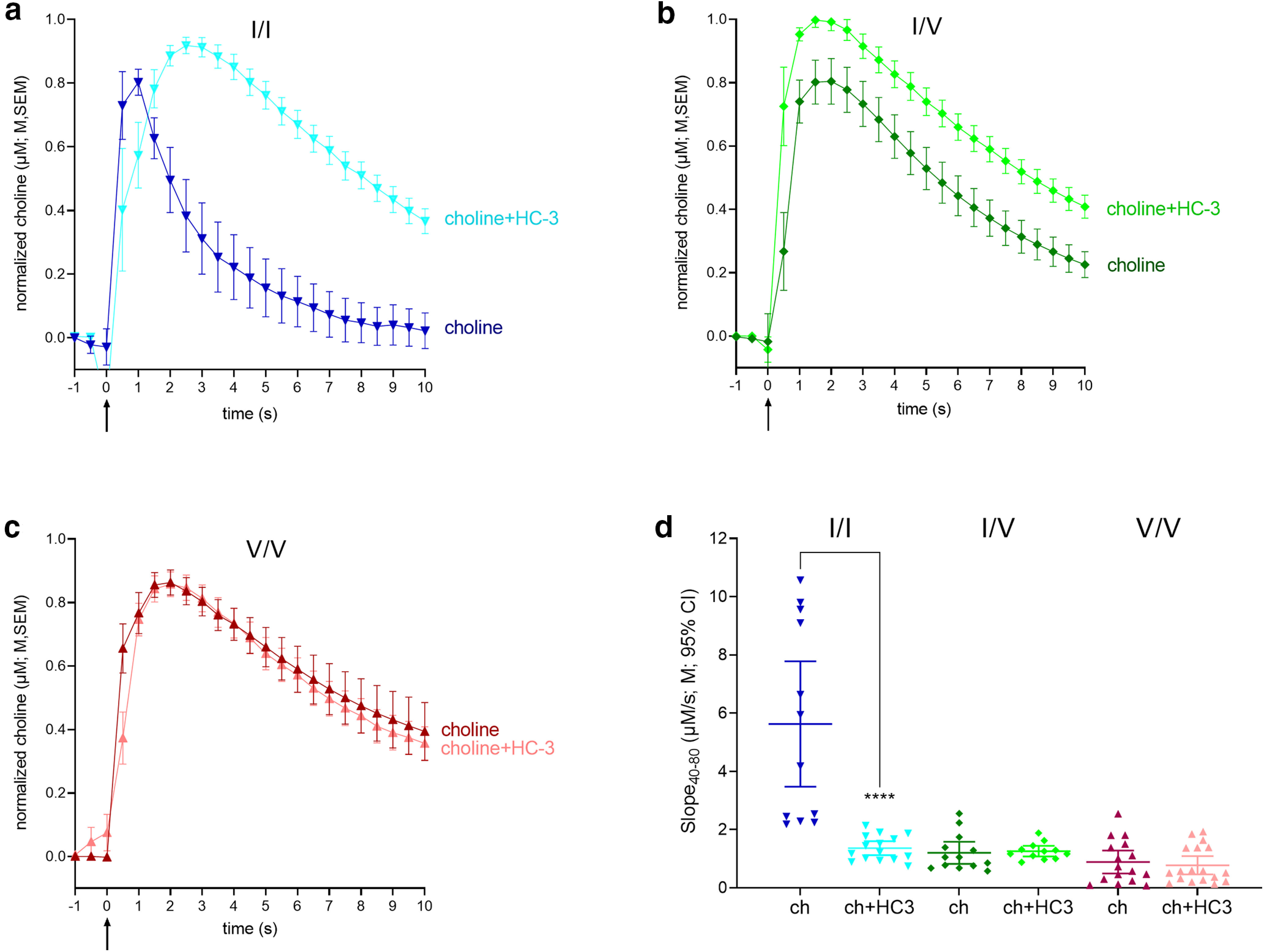
Impact of the CHT competitive inhibitor hemicholinium-3 (HC-3) on choline clearance in WT and CHT Val89 mice. a–c, Averaged traces of exogenous choline clearance with and without HC-3 (for visual clarity, traces shown here and in Fig. 4 were normalized to the peak current values; shown are means, M, and standard errors of the means, SEM). Traces and slopes in the absence of HC-3 were obtained from a separate group of mice (Fig. 2). Choline clearance in the presence of HC-3 was determined from 15 traces in WT (n = 5), 12 traces in CHT I/V (n = 4), and 18 traces in CHT V/V (n = 6), with 3 traces selected from each mouse. Darker colored lines represent choline clearance traces following pressure ejections of 5 mm choline (ch) alone, while lighter colors show clearance following ejections of a solution containing 5 mm choline and10 μm HC-3, with each solution ejected at time 0. d, Individual choline clearance rates (Slope40–80) following ejections of 5 mm choline (ch) only and a 5 mm choline and 10 μm HC-3 cocktail (ch+HC3). Only clearance rates recorded in WT mice were significantly slowed by HC-3. Following HC-3 ejections, residual clearance rates did not differ across genotypes (LSD test; d shows individual values, means, M, and 95% confidence intervals, CI).
