Figure 2.
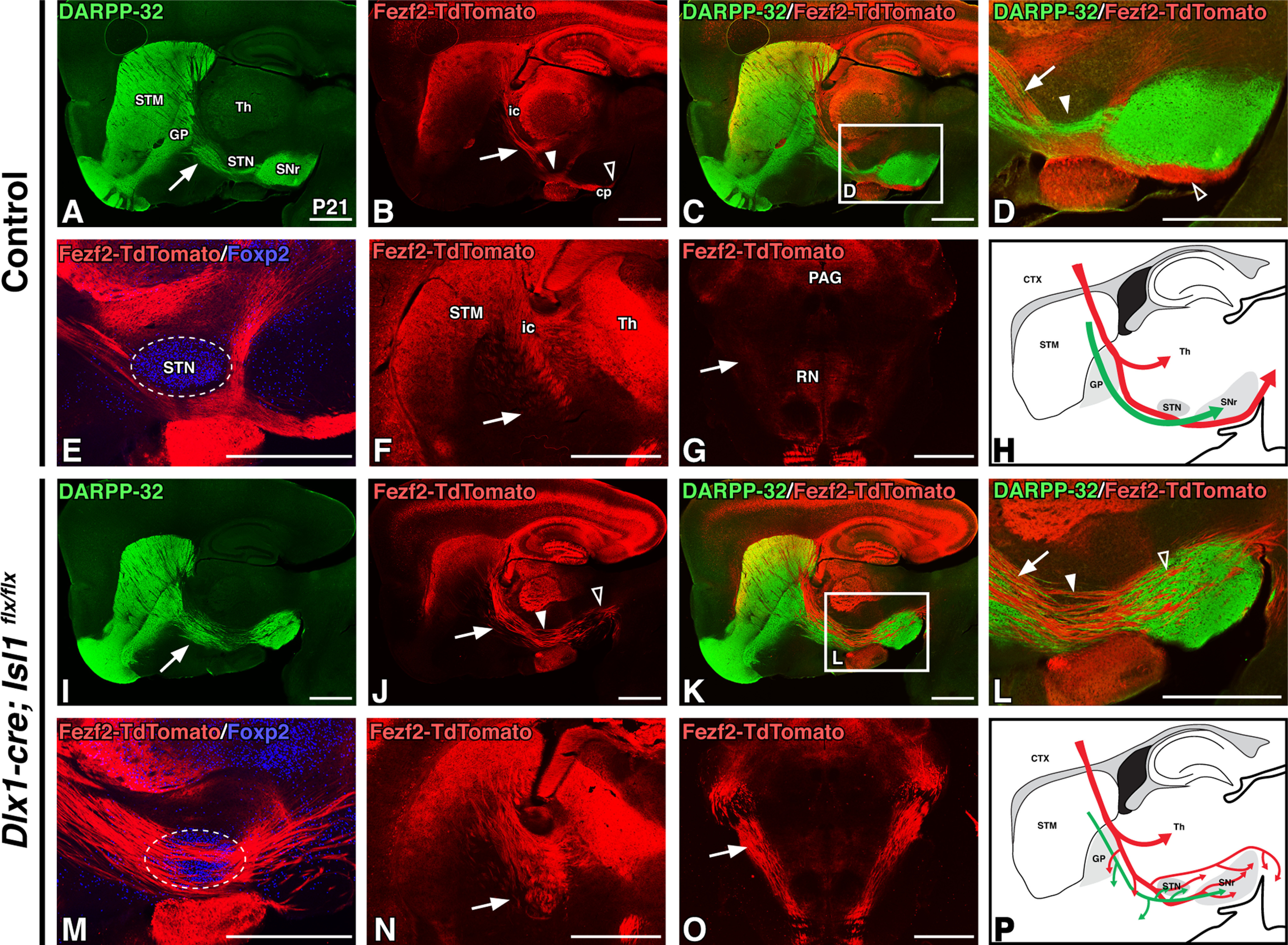
Conditional loss of Isl1 within the ventral forebrain results in postnatal corticofugal axon defects. A–E, I–M, Sagittal sections of P21 control (Dlx1-cre; Isl1flx/+; Fezf2-TdTomato or Isl1flx/flx;Fezf2-TdTomato, n = 3; A–E) and Isl1 cKO (Dlx1-cre; Isl1flx/flx; Fezf2-TdTomato, n = 3; I–M,) transgenic mouse brains. DARPP-32 labeling of striatal projections (A, I), Fezf2-TdTomato labeling of corticofugal axons (B, J), DARPP-32/Fezf2-TdTomato double-labeling at low power (C, K), DARPP-32/Fezf2-TdTomato double-labeling at high power (D, L; C, K, boxes) and Fezf2-TdTomato/Foxp2 (STN marker, boundaries outlined) double-labeling (E, M). Striatal projections (green) are disorganized in Isl1 cKOs (A, I, arrows). Corticofugal axons (red) defasciculate, exhibit ventral deviation (B, D, J, L, arrows), override the STN (E, M; B, D, J, L, solid arrowheads), and take aberrant paths through the cerebral peduncle (B, D, J, L, open arrowheads). F, G, N, O, Fezf2-TdTomato labeling in P21 coronal sections of control (F, G, n = 3) and Isl1 mutants (N, O, n = 3) at rostral (F, N) and caudal (G, O, pseudocolored DAB immunohistochemical staining) levels further illustrate disorganization, ventral misrouting (F, N, arrows), and aberrant trajectories of corticospinal axons at the pontine level (G, O, arrows). H, P, Cartoon diagrams illustrating a sagittal view of altered direct pathway (green) and corticofugal pathway (red) axon trajectories in adult Isl1 cKOs (P) compared with controls (H). cp, Cerebral peduncle; CTX, cortex; ic, internal capsule; PAG, periaqueductal gray; RN, red nucleus; STM, striatum; Th, thalamus. Scale bars, 1000 μm.
