Figure 7.
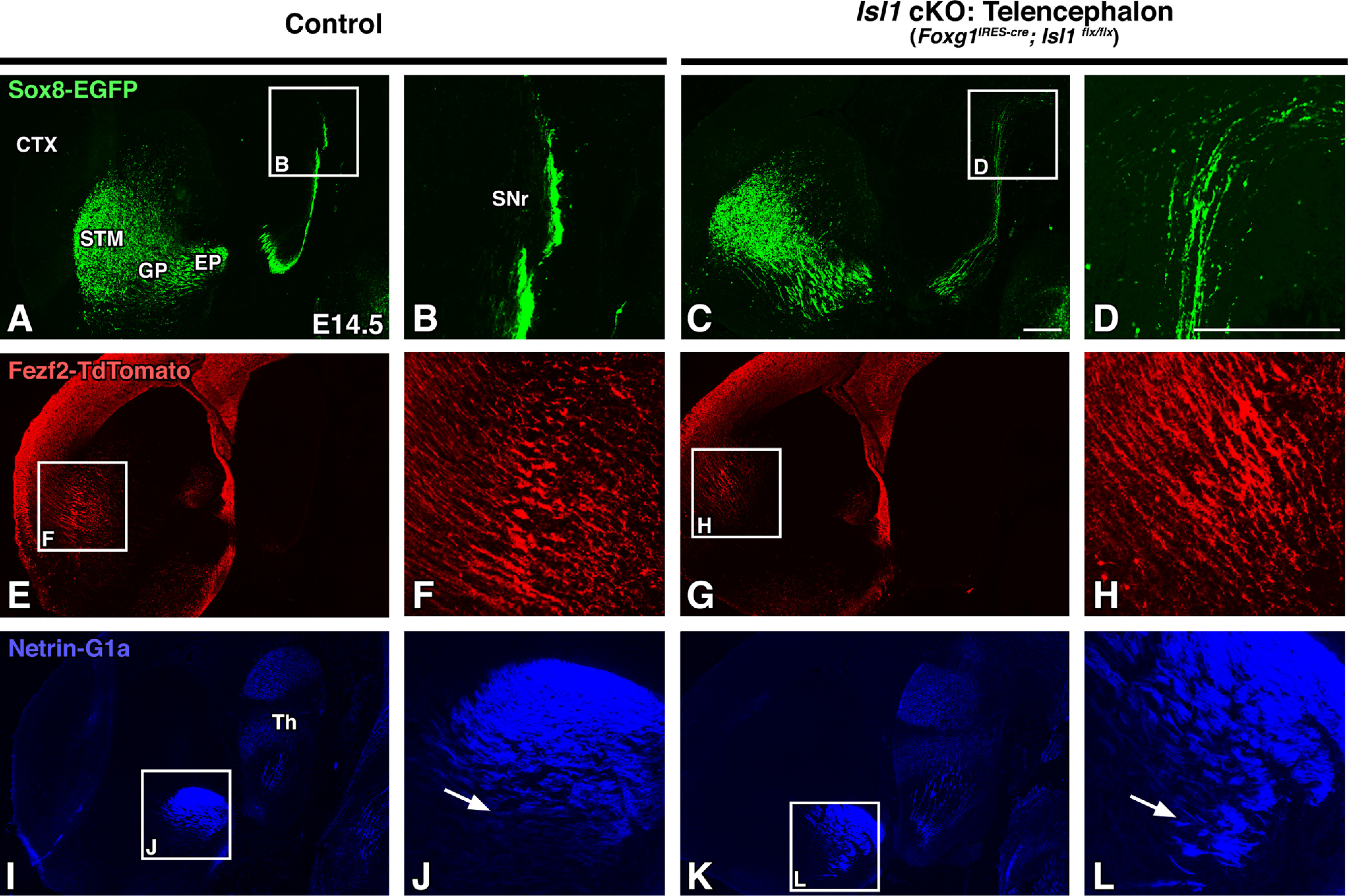
Striatonigral defects in Isl1 mutants appear before visible corticofugal defects. A–L, Sagittal brain sections of E14.5 controls (Foxg1IRES-cre; Isl1flx/+; Sox8-EGFP; Fezf2-TdTomato or Isl1flx/flx; Sox8-EGFP; Fezf2-TdTomato, n = 3; A, B, E, F, I, J) and Isl1 cKOs (Foxg1IRES-cre; Isl1flx/flx; Sox8-EGFP; Fezf2-TdTomato, n = 3; C, D, G, H, K, L) at low (A, C, E, G, I, K) and high (B, D, F, H, J, L; A, C, E, G, I, K boxes) power are shown. Sox8-EGFP labeling of direct pathway axons show that mutant striatonigral axons are disorganized as they project to the SNr (A–D). Mutant corticofugal axons appear normal at this stage as illustrated by Fezf2-TdTomato labeling (E–H). Netrin-G1a labeling of thalamocortical axons exhibit ventral misrouting and disorganization (I–L, compare J, L, arrows). CTX, Cortex; STM, striatum; Th, thalamus. Scale bars, 250 μm.
