Figure 4. Genetic deletion of CD38 decreases heart rate and increases heart rate variability in vivo, and these effects are dependent on CD38 catalytic activity suppression.
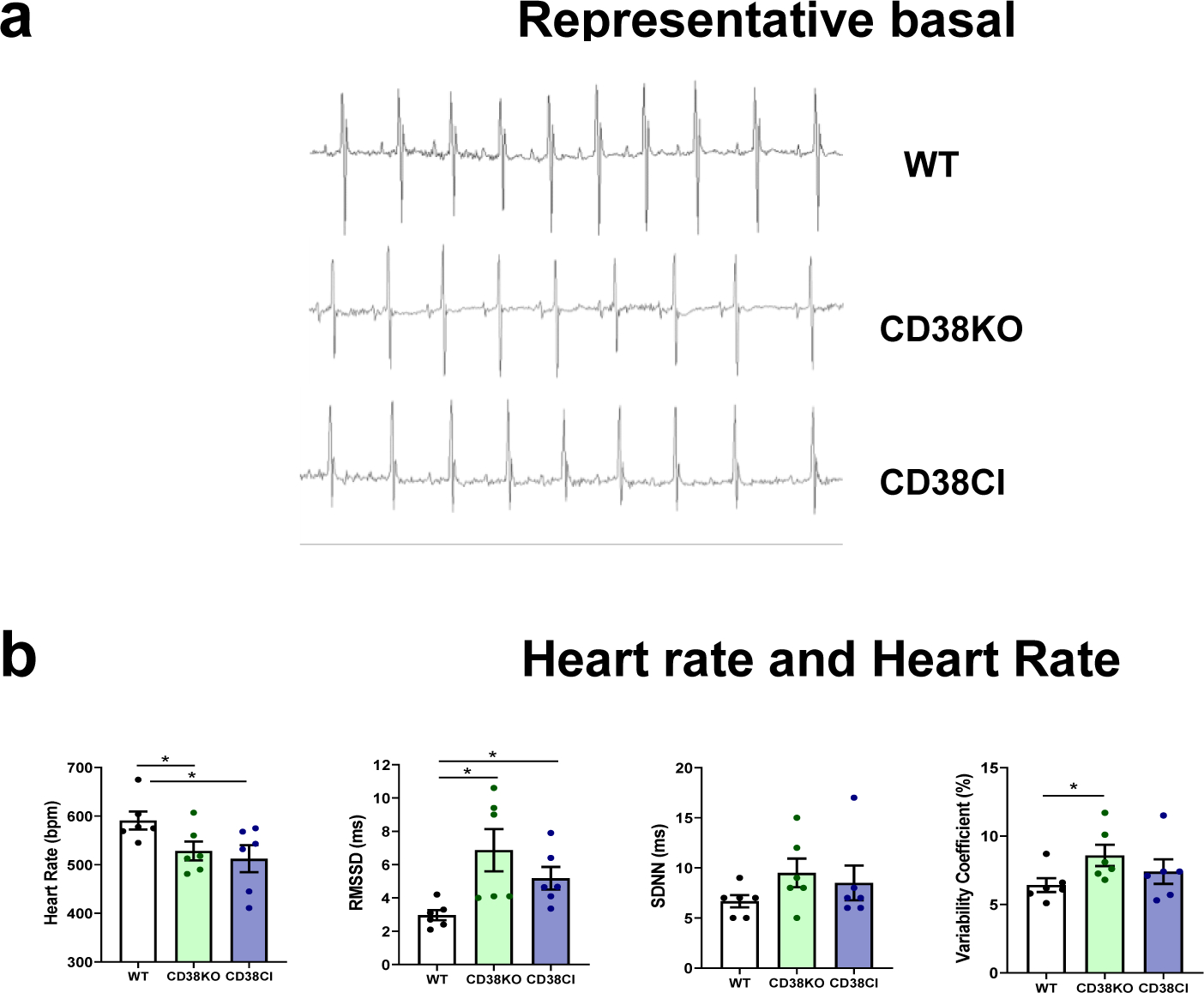
WT, CD38KO and CD38CI (catalytically inactive) male adult mice (6–8-month-old) were submitted to telemetry implant surgery and their ECG was recorded in the 3rd and 4th day after surgery. (a) Representative 1 second ECG tracings from WT, CD38KO, and CD38CI mice. (b) The graphs show heart rate (HR) and three indexes of HR variability (HRV): root mean square of successive differences (RMSSD), standard deviation of normal-normal RR intervals (SDNN), and variability coefficient (VC). HR is lower and HRV is higher in CD38KO and CD38CI groups compared to WT group. Data are mean ± SEM (N=6 mice/group), analyzed by unpaired two-sided t-test, *P<0.05.
