Figure 2. PhotoExM of intestinal organoids cultured in Matrigel.
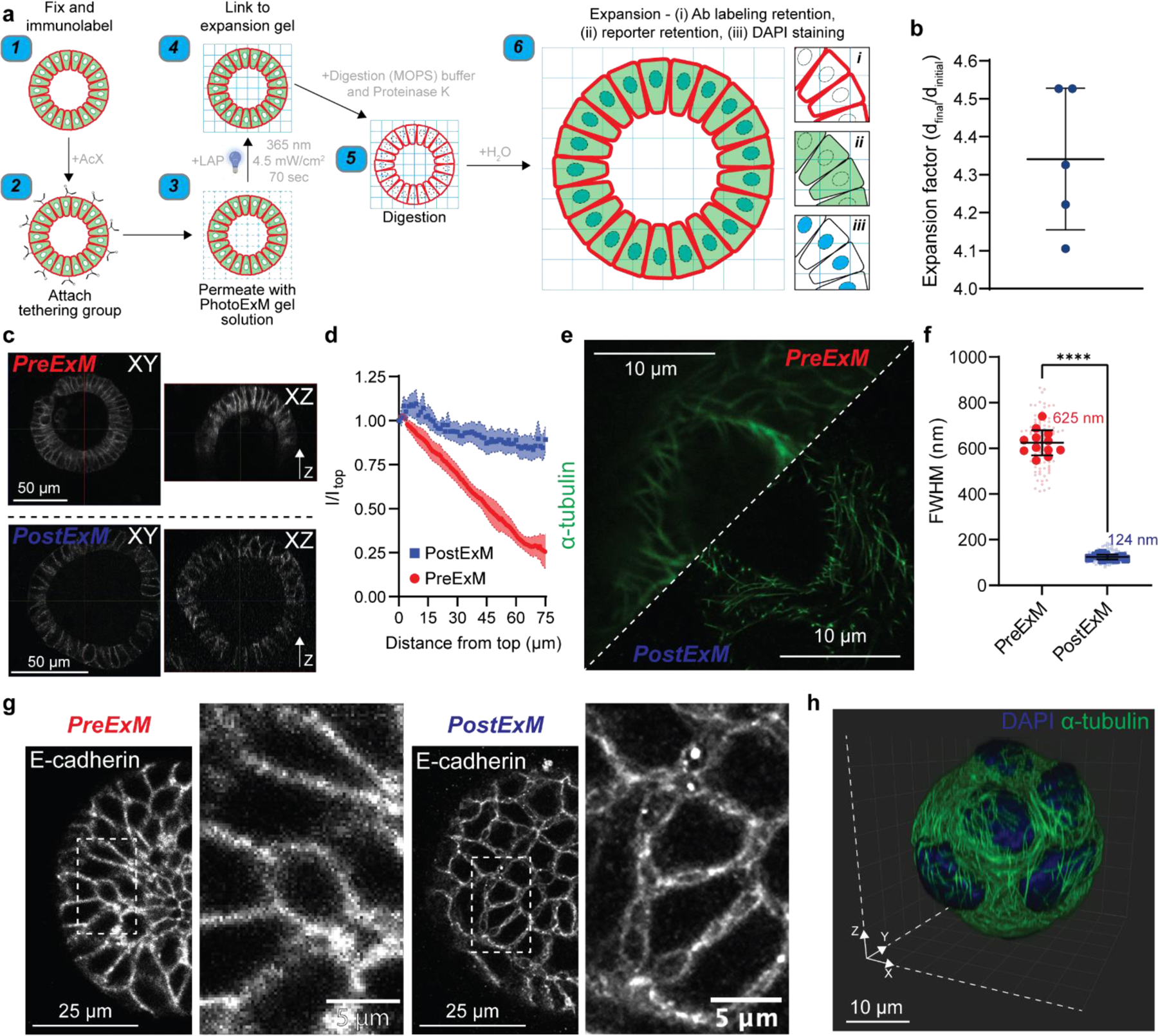
(a) Schematic for PhotoExM of intestinal organoids. Organoids are first fixed and immunolabeled using standard protocols, then the tethering group, Acryloyl X (AcX), is added. Next, the PhotoExM solution is permeated into the sample. Upon 70 s light irradiation (Io = 4.5 mW/cm2, λ = 365 nm) and the addition of a photoinitiator, LAP, the sample is linked to the expansion hydrogel. The addition of Proteinase K (16 U/mL) in the digestion buffer degrades and digests, as well as optically clears the organoids. Finally, immersion in H2O promotes dissociation of the electrolyte (sodium acrylate) monomer, resulting in physical expansion. Spatial information is retained, and immunolabeled whole organoids can be imaged in 3D. Additionally, retention of DNA allows for PostExM staining with DAPI, and retention of eGFP reporters allows for imaging of reporter organoid lines. (b) Expansion factor of organoids expanded in Matrigel. n = 5 hydrogels, graph presented as mean +/− s.d. (c) PreExM and PostExM images of E-cadherin labeled organoids. XY (single plane cross section) and XZ (orthogonal projection). (d) Fluorescent intensity of E-cadherin immunolabeling for PreExM and PostExM images across Z-stacks. Intensity normalized to the intensity at depth z=0 (Itop). The line represents the mean, with shaded regions representing 95% CI. (e) α-tubulin imaging PreExM and PostExM of organoids cultured for 2 days, starting from single cell suspensions. (f) Resolution of PreExM and PostExM samples quantified by the diameter of microtubules. n = 90–100 line scans per condition (smaller data points) across 12 individual organoids (larger data points). Graph presented as mean +/− s.d. **** p < 0.0001. (g) Single z-stack PreExM and PostExM imaging of E-cadherin. (h) 3D reconstruction in IMARIS of a whole PostExM organoid immunolabeled with α-tubulin and stained with DAPI. Organoids were cultured for 2 days, starting from a single cell encapsulation.
