Fig. 1.
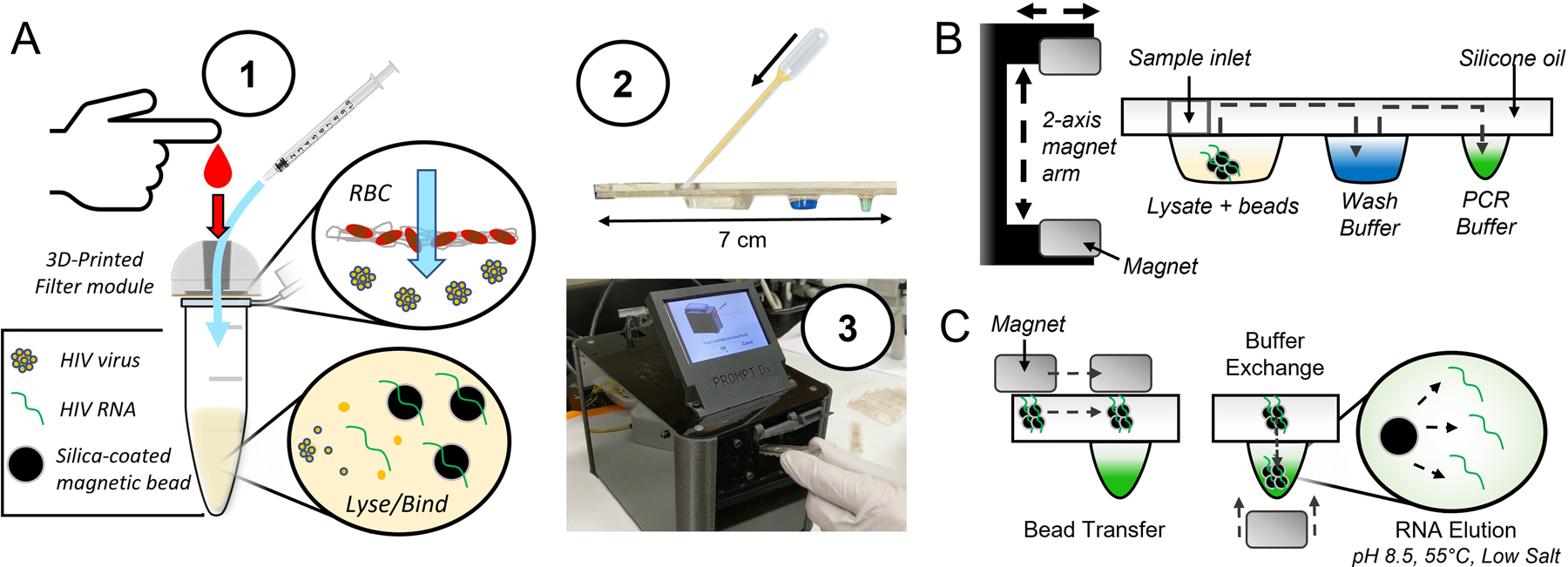
Filtration-assisted magnetofluidic blood-to-PCR workflow. A – To begin the test, (1) a droplet of blood is first deposited into the filter module and viral particles are rinsed through the filter membrane with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) using a syringe. The filter traps red blood cells (RBCs) while viral particles are small enough to pass through into a lysis and binding solution containing magnetic beads for capture of viral RNA. This entire filtered plasma mixture is (2) loaded into the assay cartridge, which is then (3) inserted into the instrument. B – The magnetic beads are transferred through an immiscible silicone oil layer into the cartridge’s extruded wells containing preloaded reagent buffers using a 2-axis motorized magnet arm. C – Bead transfer between wells is conducted by lateral movement of the top permanent magnet with bead exchange into buffers using vertical translation of the magnet arm to attract beads into the well with the bottom magnet. The final transfer of beads into the PCR buffer allows direct elution of RNA due to the relatively alkaline pH, elevated temperature, and low salt conditions.
