Fig. 3.
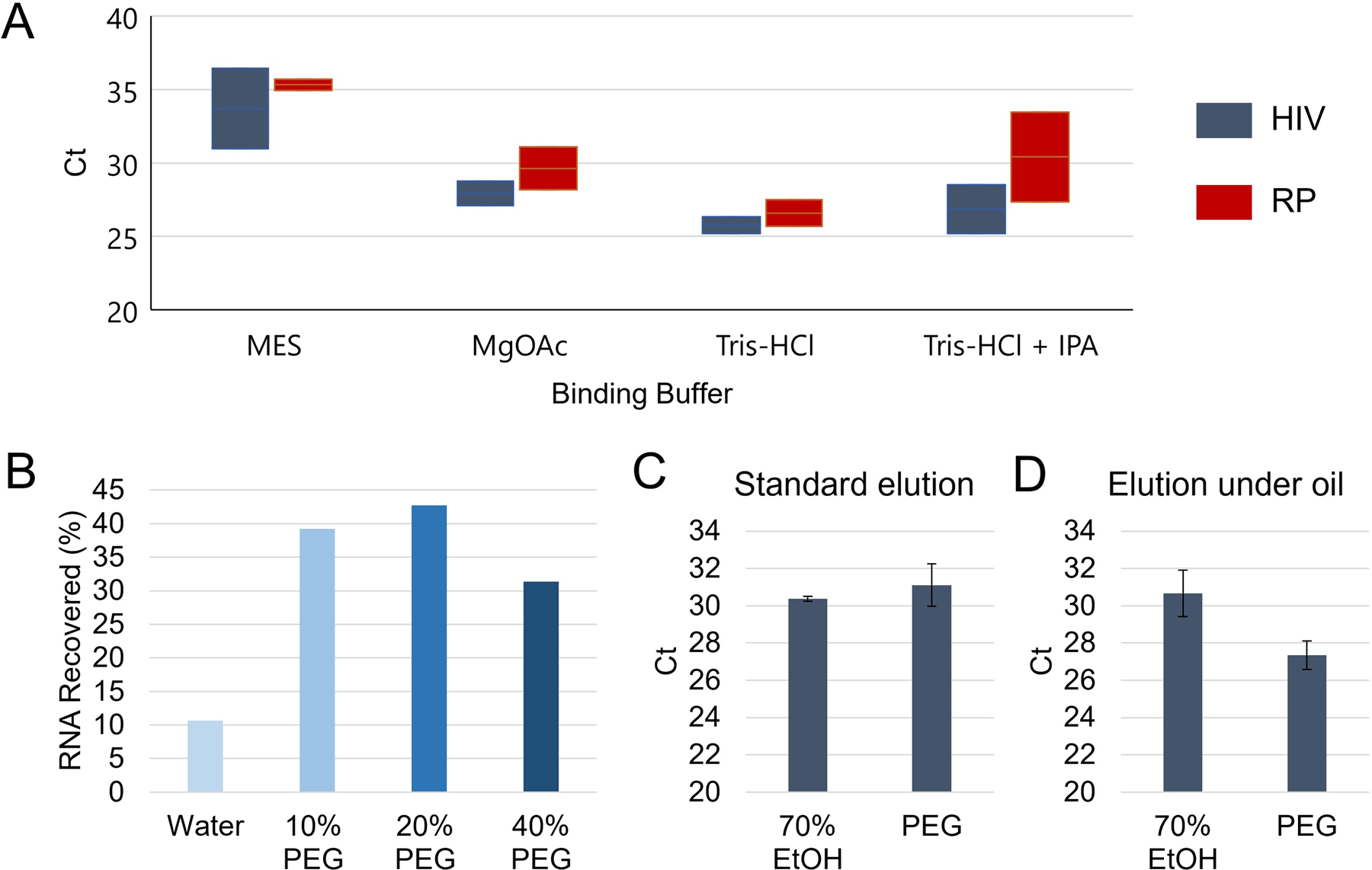
Silica bead buffer characterization. A – Ranges of Ct values for PCR amplification of HIV RNA and human RNAse P (RP) after direct elution of silica beads following blood filtration and varying binding buffer solutions with 20% w/v PEG washes (n=2). B – Aqueous solutions with polyethylene glycol (PEG) showed effective washing of silica beads while improving HIV RNA retention compared to water alone as a wash buffer. C – Compared to traditional ethanol-based washes (n=3), PEG washes (n=3) performed comparably with no significant difference in Ct for captured HIV RNA amplification (p=0.39). D – When using silicone oil to cover the silica beads during binding, wash, and elution, the PEG washes (n=3) exhibited lower Ct values (p=0.03) compared to ethanol washes (n=3) indicating superior RNA recovery.
