Figure 1.
Comparison of target DNA cleavage activity of chimeric DNA-RNA guided en-Cas12a and wt-Cas12a
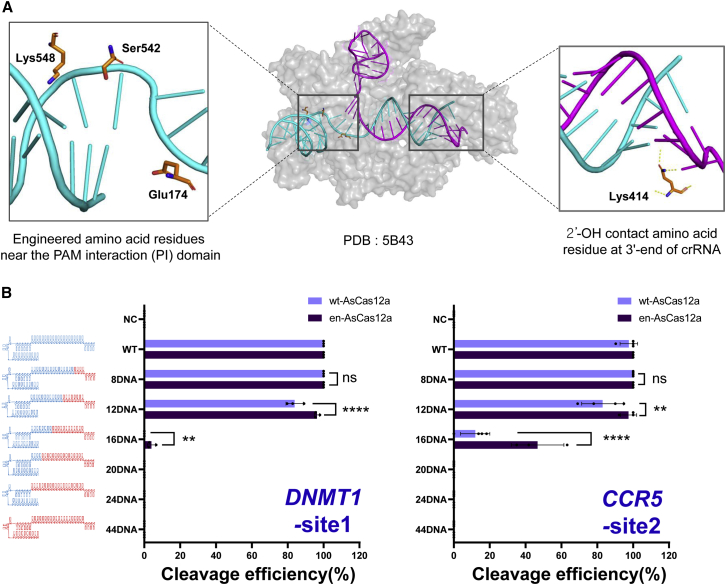
(A) Structure of the target-strand DNA-crRNA-AsCas12a complex (PDB: 5B43). Left inset: amino acids in AsCas12a interacting with around the PAM sequence in the target DNA. Right inset: amino acid (Lys414) interacting with the target-strand DNA-crRNA duplex in AsCas12a (hydrogen bonding with the 2′-OH group on the crRNA 3′ end region). (B) Comparison of cleavage efficiency of DNA amplicons using chimeric DNA-RNA guided wt-AsCas12a (light purple) and en-AsCas12a (dark purple). Each chimeric DNA-RNA includes target nucleotide sequences (DNMT1, CCR5-site2) with gradual DNA substitution from the 3′ end of crRNA. NC, negative control; WT, wild-type crRNA was treated with wt- or en-AsCas12a. The RNA region of the (cr)RNA is shown in blue, and the substituted DNA region is shown in red (8DNA to 44DNA indicates number of substituted DNA nucleotides in (cr)RNA). The x axis indicates the efficiency of the target gene (DNMT1-site1, CCR5-site2) cleavage by wt- and en-AsCas12a using various chimeric DNA-RNA guides (gradual DNA substitution from the 3′ end of the (cr)RNA). All cleavage efficiencies were calculated from band intensity, which was separated on 2% agarose gel (cleaved fragment intensity [%]/total fragment intensity [%]). All calculated values were normalized to wild-type (cr)RNA (Figure S2). The histograms represent means ± SEM from three independent experimental values. p values were calculated using two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (ns, not significant; ∗p < 0.0332, ∗∗p < 0.0021, ∗∗∗p < 0.0002, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).